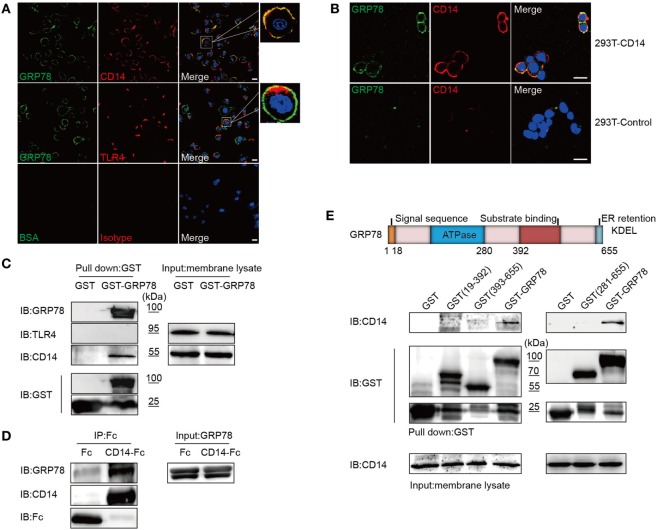
Figure 4.
GRP78 Interacts with CD14. (A) DC2.4 cells were treated with AF488-GRP78 (green) for 1 h at 4°C, and then TLR4 and CD14 (red) were stained. (B) pcDNA3.1-CD14 transiently transfected HEK293T cells were incubated with AF488-GRP78 and then CD14 was stained. Fluorescence localization was determined by confocal laser scanning microscopy. (C) Immunoblotting of the interaction of proteins with GST-GRP78, after incubation with membrane lysates of DC2.4 cells, followed by precipitation by glutathione agarose beads. (D) Protein precipitation study of CD14-Fc with GRP78. The cDNA encoding mouse CD14 was cloned into the pOptiVEC-hIgG1-Fc vector. Recombinant CD14-Fc and Fc control proteins from culture supernatants of HEK293T cells transiently transfected with plasmids were immobilized onto protein G-agarose, followed by incubation with GRP78 at 4°C overnight. The precipitates were immunoblotted using antibody specific for hIgG1-Fc, GRP78, and CD14. (E) Schematic representation of recombinant GRP78 (upper). Interaction of GRP78 fragments (amino acids in parentheses) with CD14 was assessed by GST precipitation, as described in (D). All images for all panels are representative of at least three independent experiments in which > 100 cells were examined and > 95% of cells showed similar staining. Scale bar, 20 µm.