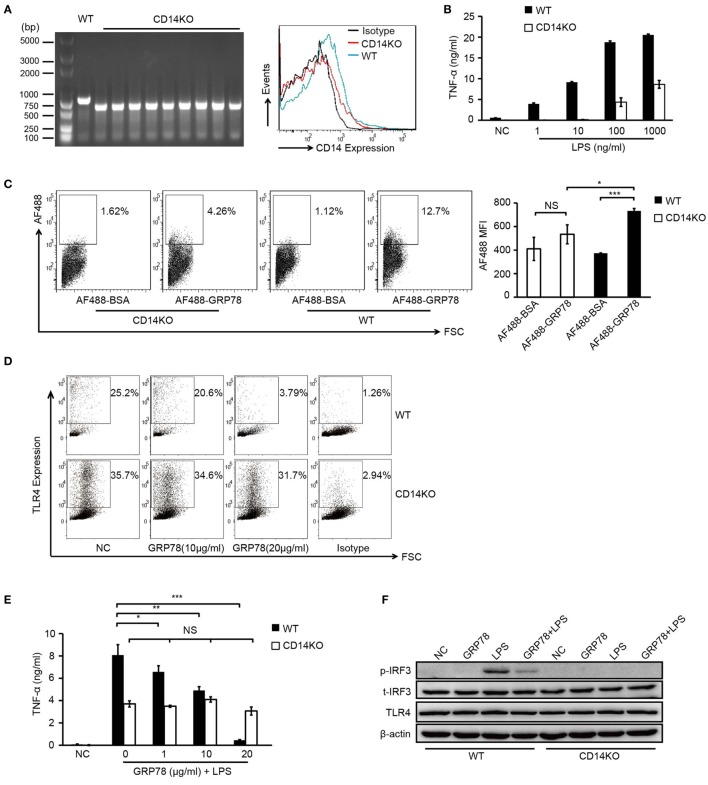
Figure 5.
GRP78-induced TLR4 endocytosis is CD14 dependent. (A) CD14 levels on WT and CD14KO bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) were determined by PCR (left) and FCM (right). PCR products of CD14 gene in the genomic DNA from WT and CD14KO mouse: CD14 knockout = ~600 bp, wild type = 840 bp (according to the Jackson Laboratory). (B) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) of TNF-α in WT or CD14KO BMDCs stimulated for 4 h by LPS at the concentrations indicated. (C) FCM analyses for GRP78 binding with WT or CD14KO BMDCs. Representative dot plots (left) and MFI (right) are shown. (D) WT or CD14KO BMDCs were treated with 10 µg/mL or 20 µg/mL GRP78 for 30 min. Surface TLR4 was determined by FCM. (E) ELISA of TNF-α in WT or CD14KO BMDCs treated with LPS (100 ng/mL) and GRP78 for 4 h. (F) WT or CD14KO BMDCs were stimulated with GRP78 (20 µg/mL), LPS (100 ng/mL), or mixtures of GRP78 and LPS at 37°C for 30 min, cells were lysed, and phoepho-IRF3, total-IFR3, TLR4, and actin were detected by immunoblotting. Error bars represent mean ± SD from triplicate samples in one experiment. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.