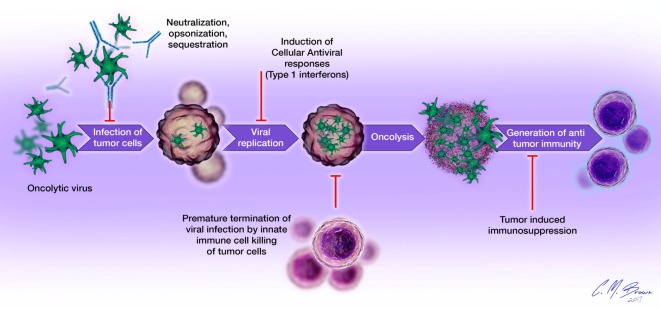
Figure 2.
Immunologic barriers to successful oncolytic virotherapy: (1) oncolytic virus delivery to tumor sites is impeded by the presence of neutralizing antibodies, complement proteins, and sequestration in organs such as the liver and spleen; (2) cellular antiviral responses, such as type I interferon signaling limits viral replication within tumor cells; (3) destruction of infected tumor cells by cells of the innate immune system (neutrophils, macrophages, NK cells) prematurely terminates viral infection; (4) tumor-induced immunosuppression (elaboration of immunosuppressive cytokines, accumulation of regulatory T cells, overexpression of negative checkpoint regulators of T cell function) inhibits the generation and effector functions of antigen-specific antitumor immune responses.