Table 1. Changes in binding free energies for TEM1 and BLIP upon mutation.
| TEM1 mutants
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BLIP mutants | WT | E104A* | Y105A* | E104A, Y105A* | R243A† | K234A† | S130A† | SSR† | KSSR† |
| WT | 0.0 | 6.5 | –0.7 | 4.3 | 5.3 | 4.3 | 1.4 | 7.3 | 10.2 |
| D49A† | 7.5 | 4.6 | 6.7 | 1.5 | 3.7 | 7.1 | |||
| K74A* | 14.9 | 6.6 | 13.9 | 5.8 | 27.7 | 27.4 | 13.3 | 21.0 | 22.9 |
| F142A* | 8.8 | 11.5 | 2.9 | 6.3 | 14.2 | 14.2 | 11.9 | 14.8 | 17.9 |
| Y143A* | 1.6 | 7.8 | 4.5 | 8.6 | 9.5 | 10.7 | 7.5 | 11.1 | 15.4 |
| K74,F142A* | 20.3 | 13.1 | 20.0 | 13.1 | 23 | 24.4 | 21.6 | 24.3 | 23.7 |
| K74A,Y143A* | 12.8 | 4.4 | 14.2 | 7.4 | 18.3 | 20.4 | 15.6 | 18.4 | 27.7 |
| F142A,Y143A* | 11.9 | 12.1 | 12.5 | 11.9 | 19.0 | 19.6 | 17.4 | 20.0 | 20.4 |
| K74A,F142A,Y143A* | 16.3 | 10.0 | 17.7 | 10.1 | 22.0 | 22.9 | 21.2 | 23.2 | 22.9 |
Binding energies (in kJ/mol) were measured with TEM1 proteins immobilized to the sensor chip. The average standard deviation in the value of ΔΔGKA(ma) is ± 0.5 kJ/mol. KA(ma) is the equilibrium affinity constant derived by action mass analysis (see Materials and Methods). The change in free energy upon mutation, ΔΔGKA is calculated from RT In (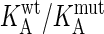 ) in kJ/mol. SSR protein, TEM1 mutated to S130A, S235A, and R243A. KSSR protein, TEM1 mutated to S130A, S235A, R243A, and K234A. Underlined in bold are the two multiple mutants where entire clusters were removed.
) in kJ/mol. SSR protein, TEM1 mutated to S130A, S235A, and R243A. KSSR protein, TEM1 mutated to S130A, S235A, R243A, and K234A. Underlined in bold are the two multiple mutants where entire clusters were removed.
Mutations located in C2
Mutations located in C1
