FIG 5.
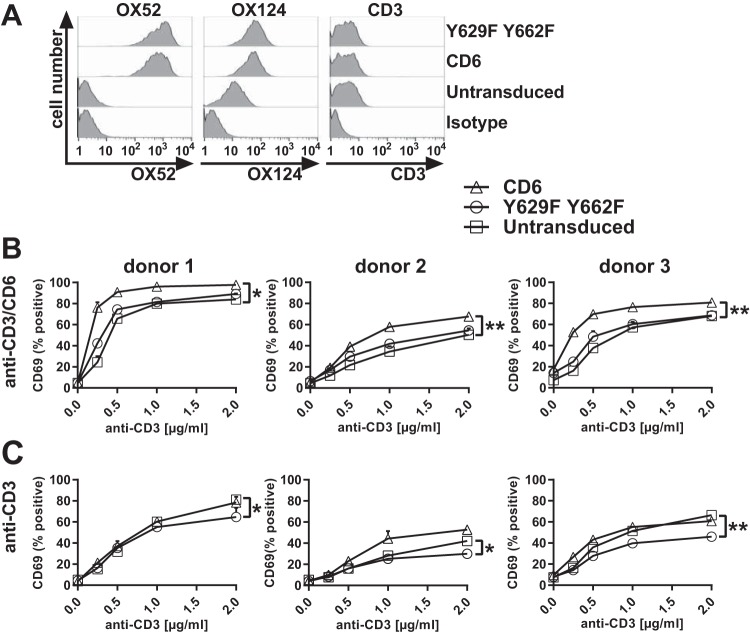
Costimulation by CD6 is dependent on CD6 Y629 and Y662 in primary CD4+ T cells. Flow cytometry analysis of primary CD4+ T cells transduced with rat domain 1-containing human CD6 or the Y629F Y662F double mutant protein fused to EGFP. (A) Cells stained with a rat domain 1-containing CD6 MAb (OX52) (left), a human domain 3-containing CD6 MAb (OX124) (middle), and a CD3 MAb (UCHT1) (right) show that there are similar levels of CD6 expression on transduced T cell blasts with ∼40-fold-higher MFIs and that CD3 levels in T cells were unchanged compared with those in untransduced cells. Negative isotype controls are shown for each MAb. (B and C) Cells were stimulated with different concentrations of CD3 MAb with (B) and without (C) CD6 MAb (OX52) (5 μg/ml) and measured for the percentage of CD69+ EGFP-positive cells. Compared with those for untransduced cells, the percentages of CD69+ cells were increased in cells transduced with CD6, but the effect of CD6 was reduced by the Y629F Y662F double mutation. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. Combined data from three experiments (means ± standard errors of the means) are shown. The unpaired Student t test was used to compare the Emax values of each dose-response curve.