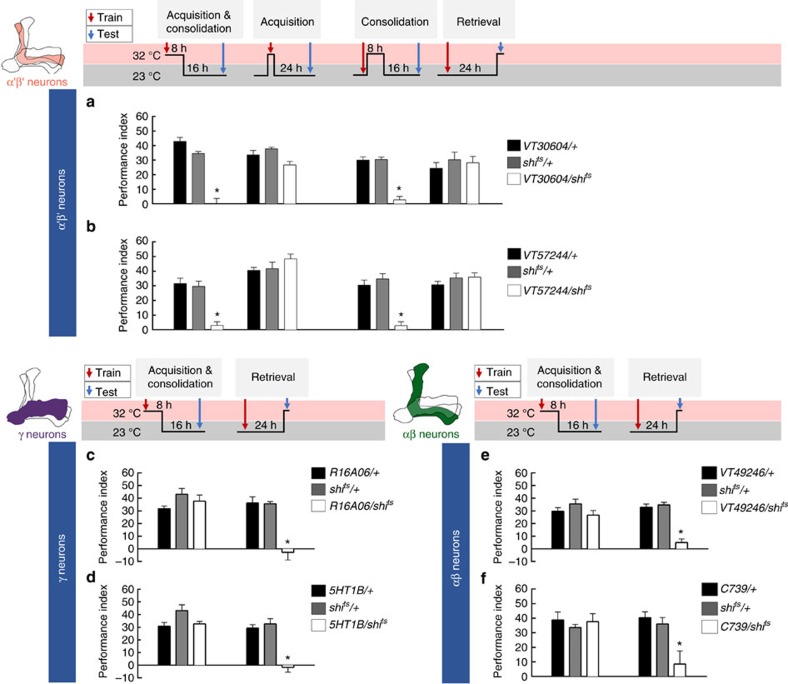
Figure 6. MB neural subsets play distinct roles during LTM processing.
(a) Blocking the output of α′β′ neurons (VT30604-GAL4) using shits during consolidation but not during acquisition or retrieval, impaired LTM. Each value represents mean±s.e.m. (N=8 for each bar). *P<0.05; analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey's test. (b) Blocking the output of α′β′ neurons (VT57244-GAL4) using shits during consolidation but not during acquisition or retrieval, impaired LTM. Each value represents mean±s.e.m. (N=8 for each bar). *P<0.05; ANOVA followed by Tukey's test. (c) Blocking the output of γ neurons (R16A06-GAL4) using shits during retrieval but not during acquisition and consolidation, impaired LTM. Each value represents mean±s.e.m. (N=8 for each bar). *P<0.05; ANOVA followed by Tukey's test. (d) Blocking the output of γ neurons (5HT1B-GAL4) using shits during retrieval, but not during acquisition and consolidation, impaired LTM. Each value represents mean±s.e.m. (N=8 for each bar). *P<0.05; ANOVA followed by Tukey's test. (e) Blocking the output of αβ neurons (VT49246-GAL4) using shits during retrieval but not during acquisition and consolidation, impaired LTM. Each value represents mean±s.e.m. (N=8 for each bar). *P<0.05; ANOVA followed by Tukey's test. (f) Blocking the output of αβ neurons (C739-GAL4) using shits during retrieval but not during acquisition and consolidation, impaired LTM. Each value represents mean±s.e.m. (N=8 for each bar). *P<0.05; ANOVA followed by Tukey's test.