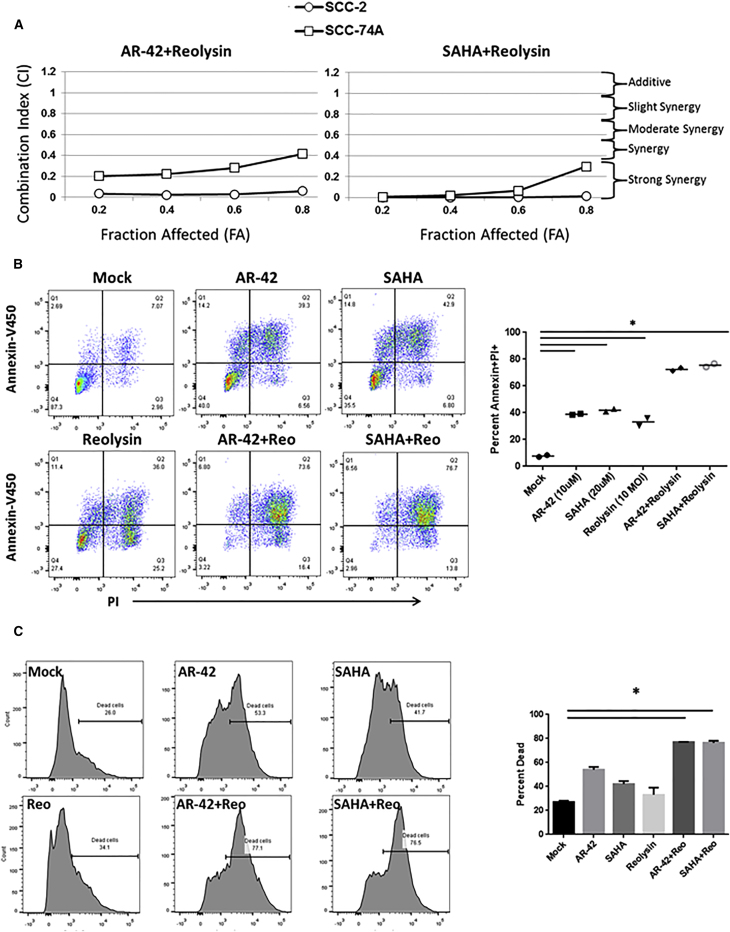
Figure 2.
HDACi and Reolysin Combination Treatment Results in Synergistic Killing via Apoptosis Induction
The impact of HDACi (AR-42 or SAHA) and Reolysin (Reo) combinatorial therapy was assessed on human (SCC-2 and SCC-74-A) and murine (MTE) squamous carcinoma cell killing and apoptosis. (A) Human head and neck cancer cell lines were treated with 0.0625, 0.125. 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 times the IC50 concentration of each HDACi and/or Reolysin for 48 hr followed by a standard MTT assay. A Chou-Talalay analysis of combinatorial killing percentages is indicated with the fraction affected (FA) versus combination index (CI) plots. CI < 1 indicates synergy, CI = 1 indicates additive, and CI > 1 indicates antagonistic combination interactions. (B) Representative propidium iodide (PI) and Annexin-V450 scatterplots and quantification of SCC-74A head and neck cancer cells treated with PBS, AR-42, SAHA, Reolysin or the combination of each HDACi plus Reolysin for 48 hr. The right panel shows the quantification of apoptosis for SCC-74A-treated cells as indicated (n = 2/group). (C) MTE murine squamous carcinoma cells were treated with AR-42 (10 μM) or SAHA (20 μM) and/or 10 MOI of Reolysin for 48 hr. Tumor cell killing was then assessed via live and dead cell staining. Representative live/dead cell histograms from flow cytometric analysis and quantification of dead cells. *p ≤ 0.01 (combination treatment differences compared to each individual treatment group). All experiments were performed in triplicate.