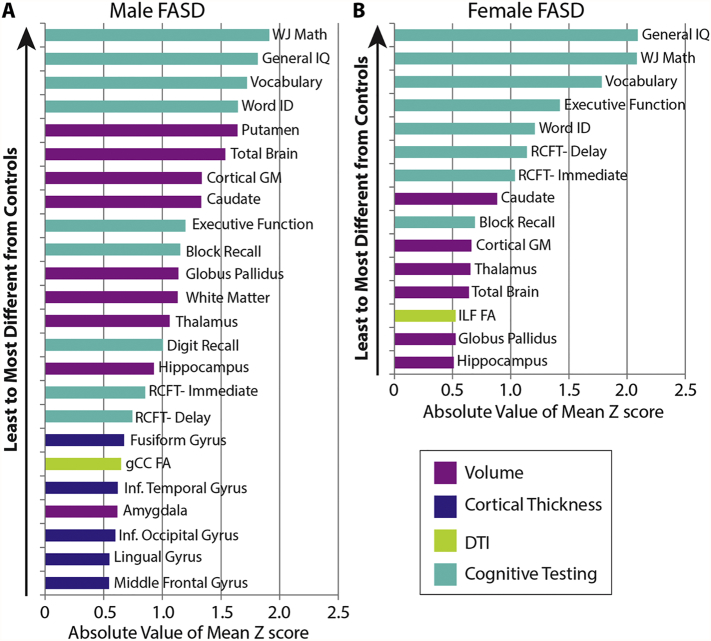
Fig. 4.
Rank ordered FASD group Z scores in males (A) and females (B) of variables with Z scores greater than an arbitrary cut-off of ± 0.5. More variables meet this criterion in males (24) than females (15). In addition, larger magnitude Z scores are seen in males relative to females for several structures. Cognitive scores are shown to have the largest absolute volume Z scores in both males and females, though it should be noted that all participants have an FASD diagnosis that requires significant cognitive impairment a priori.