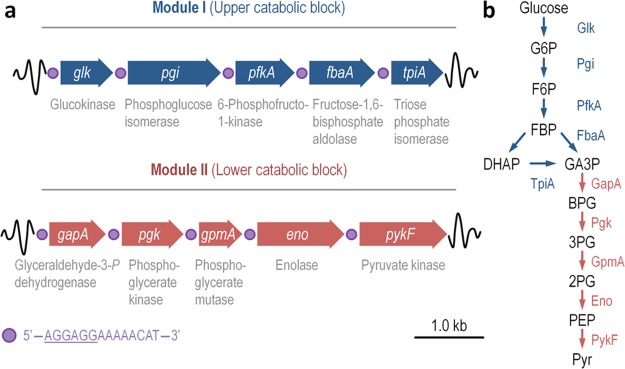
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the GlucoBrick platform layout and the cognate glycolytic reactions. (a) The minimal set of genes from Escherichia coli K-12 needed for the activation of a functional and linear Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway were edited according to the Standard European Architecture Vector rules and assembled into two synthetic operons. The first operon, termed Module I, encodes all the reactions within the upper catabolic block of the pathway (i.e., bioreactions of the preparatory phase of glycolysis). The second operon, termed Module II, spans the reactions of the lower catabolic block of the pathway (i.e., bioreactions of the pay-off phase of glycolysis). All the glycolytic reactions are shown below the gene encoding them. Note that each gene is preceded by a synthetic regulatory element, indicated by a purple circle, composed of a ribosome binding site (sequence underlined) and a short spacer sequence. (b) Linear glycolytic pathway encoded by the GlucoBrick platform, transforming glucose into glyceraldehyde-3-P (GA3P) by means of the activities of Module I; and GA3P into pyruvate (Pyr) by means of the activities of Module II. The two sets of glycolytic transformations are indicated with blue and red arrows, representing the genes within Modules I and II, respectively. Other abbreviations used in this outline are as follows: G6P, glucose-6-P; F6P, fructose-6-P; FBP, fructose-1,6-P2; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone-P; BPG, glycerate-1,3-P2; 3PG, glycerate-3-P; 2PG, glycerate-2-P; and PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate.