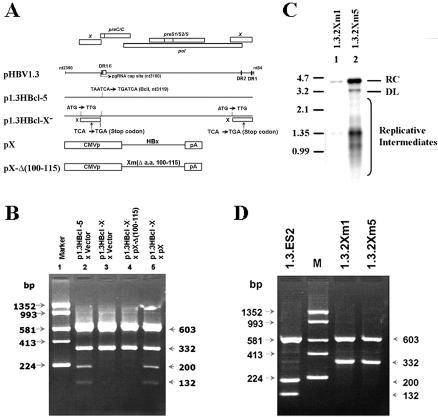
FIG. 5.
The trans-activation function of HBx is required for cccDNA transcription. (A) Scheme for construction of the HBx− construct derived from p1.3HBcl-5 and an HBx mutant with the trans-activating domain truncated [pX-Δ(100-115)]. (B) HepG2 cells were cotransfected with the indicated plasmids. Three days posttransfection, total RNAs were extracted for RT-PCR with the primer pair HBV2338/F-T20-Taq/HBV5. After SspI/BclI double digestion and electrophoresis on a 2% agarose gel, the transcriptional ability of the cccDNA was measured by the relative intensities of restricted PCR products. (C) Cytoplasm replicative intermediates of 1.3.2Xm1 and 1.3.2Xm5 were extracted for determination of their replicative capacities by Southern blot analysis. (D) Total RNAs of stable HBx-null lines were extracted, and the expression profiles of viral transcripts were determined by RT-PCR combined with SspI/BclI double digestion. The electrophoresis results showed no transcriptional activity from cccDNA in HBx-null mutants 1.3.2Xm1 and 1.3.2Xm5.