Figure 2.
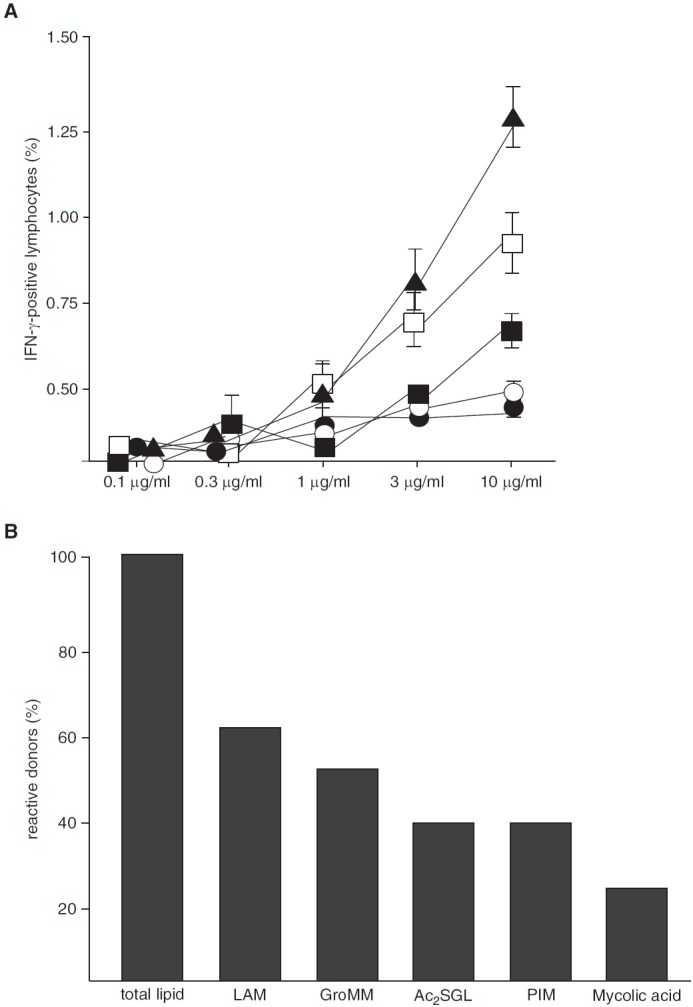
Antigen-specific T-cell activation by purified mycobacterial lipids. (A) Nonadherent peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and autologous CD1+ antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (3:1 ratio) were incubated with purified lipid antigens as indicated (solid triangles, lipoarabinomannan [LAM]; open boxes, glycerol monomycolate [GroMM); solid boxes, diacylated sulfoglycolipid [Ac2SGL]; open circles, phosphatidyl inositol mannan [PIM]; solid circles, mycolic acid). After overnight incubation, brefeldin was added for the final 4 hours of incubation. The frequency of CD3+/IFN-γ+ T cells was determined by flow cytometry. Experiments were performed in triplicates. Error bars show the SD. The figure shows a representative result of five different donors. (B) Nonadherent PBMCs and autologous CD1+ APCs (ratio 3:1) obtained from PPD+ individuals were incubated with total lipid or purified lipid antigens (10 μg/ml). IFN-γ concentration in the supernatant was measured by ELISA after 18 hours. Donors were scored positive if lipid-induced IFN-γ release was threefold greater than the unstimulated control. The number of donors responding to total lipid (n = 65) was set as 100%. The figure gives the percentage of total lipid-responsive donors that responded to the purified lipids.
