Figure 6.
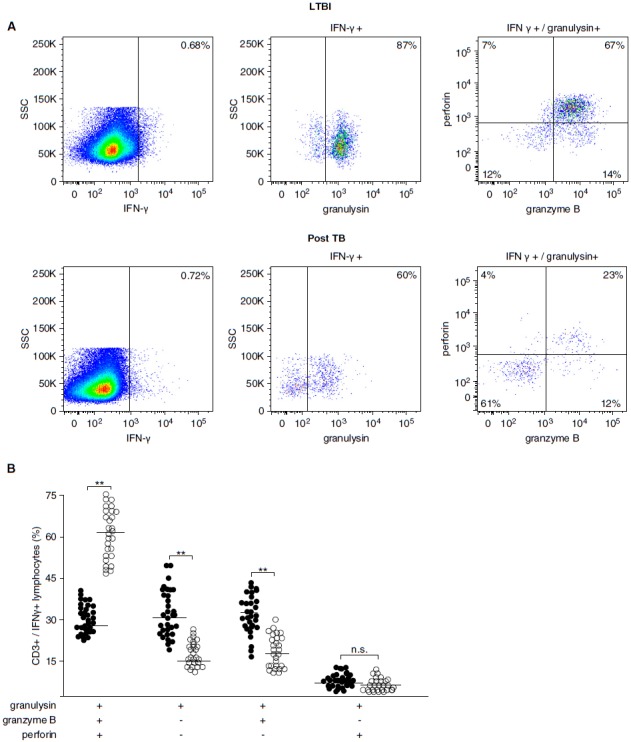
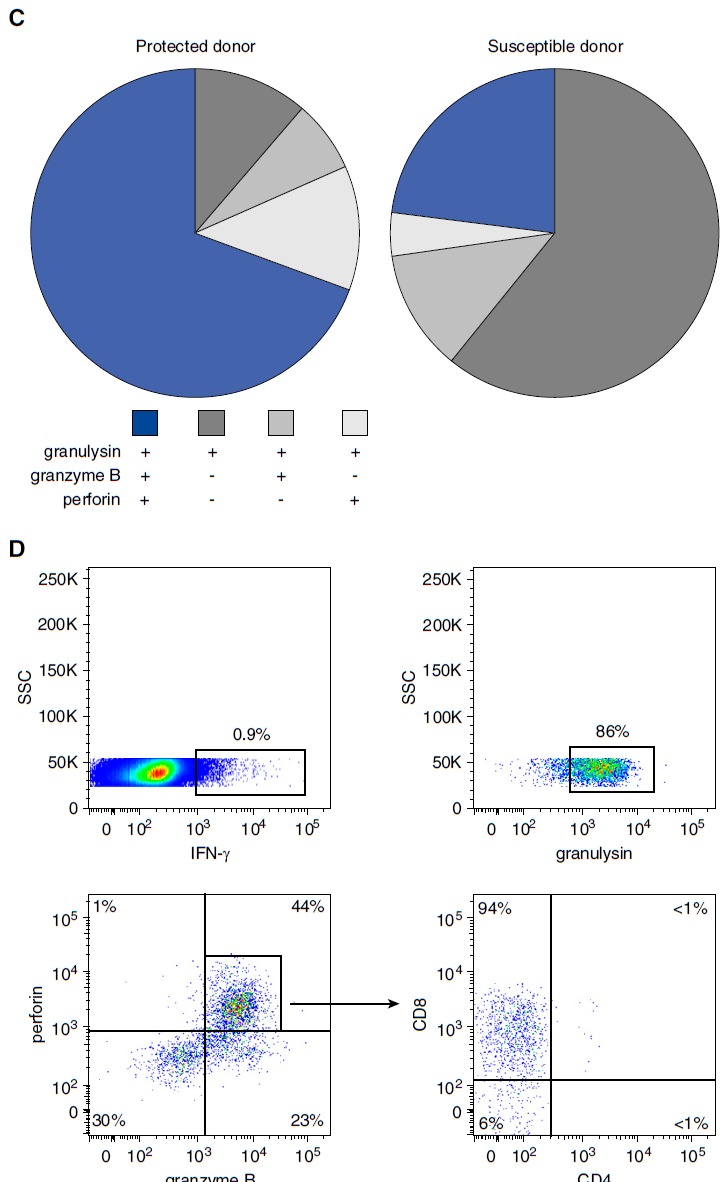
Frequency and phenotype of lipoarabinomannan (LAM)-responsive polycytotoxic T cells in latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) and posttuberculosis (post-TB) donors. A total of 10 × 106 nonadherent peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and autologous CD1+ antigen-presenting cells (APCs) (3:1 ratio) were stimulated with LAM (10 μg/ml) for 18 hours. Brefeldin was added for the final 4 hours of incubation. Cells were then stained for CD3, IFN-γ, granulysin, granzyme B, and perforin. At least 1 × 106 cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) A representative result for LTBI donors (n = 28) and post-TB patients (n = 51) is shown. (B) The individual results of all donors investigated (solid circles, post-TB; open circles, LTBI) are shown. Statistical significance was calculated using the Mann–Whitney U test (**P < 0.0001). Horizontal bars represent the mean values. (C) The pie charts present a summary of the individual data shown in (B). (D) Nonadherent PBMCs and CD1+ APCs were stimulated as described above, and CD3+/IFN-γ+ polycytotoxic T cells were further characterized by CD4 and CD8 labeling. At least 3 × 106 cells were acquired for each sample. The graph presents one representative result of three different donors. n.s. = not significant; SSC = side scatter.
