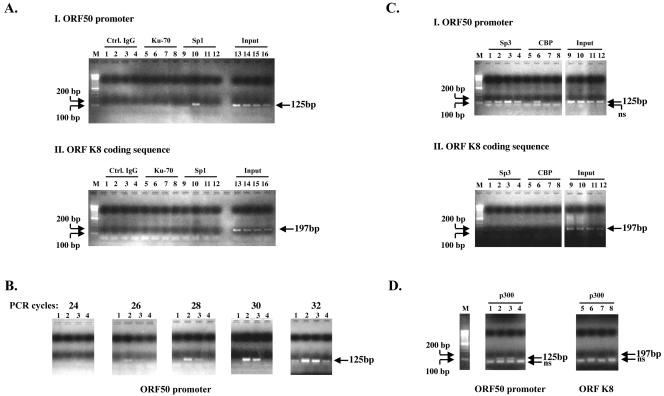
FIG. 7.
Butyrate induces transient association of Sp1 and CBP/p300 with the ORF50 promoter. (A) ChIP experiments exploring the temporal association of Sp1, CBP, and p300 with the ORF50 promoter in HH-B2 cells after butyrate induction. Immunoprecipitation was performed with normal goat immunoglobulin G (control [Ctrl]) (lanes 1 to 4), goat antibody to Ku-70 (lanes 5 to 8), goat antibody to Sp1 (lanes 9 to 12), or input DNA representing 5% of the sample (lanes 13 to 16). Cells were harvested at 0 h (lanes 1, 5, 9, 13), 4 h (lanes 2, 6, 10, 14), 11 h (lanes 3, 7, 11, 15), or 24 h (lanes 4, 8, 12, 16) after butyrate treatment. PCR primers detected the ORF50 promoter (I) or the K8 coding sequence (II). (B) The samples immunoprecipitated with antibody to Sp1 were analyzed with primers from the ORF50 promoter by using increasing numbers of PCR cycles. Samples were obtained 0 h (lane 1), 4 h (lane 2) 11 h (lane 3), or 24 h (lane 4) after butyrate treatment. (C) ChIP experiment exploring the association of Sp3 and CBP with the ORF50 promoter. M, marker; lanes 1 to 4, rabbit anti-Sp3; lanes 5 to 8, rabbit anti-CBP; lanes 9 to 12, 5% input. Samples were harvested at 0 h (lanes 1, 5, 9), 4 h (lanes 2, 6, 10), 11 h (lanes 3, 7, 11) and 24 h (lanes 4, 8, 12) after butyrate treatment. Primers specific for ORF50 promoters (I) or the K8 coding sequence (II) were used. (D) Transient association of p300 with the ORF50 promoter. ChIP experiment with antibody to p300. Samples were taken 0, 4, 11, and 24 h (lanes 1 to 4, respectively) after butyrate treatment.