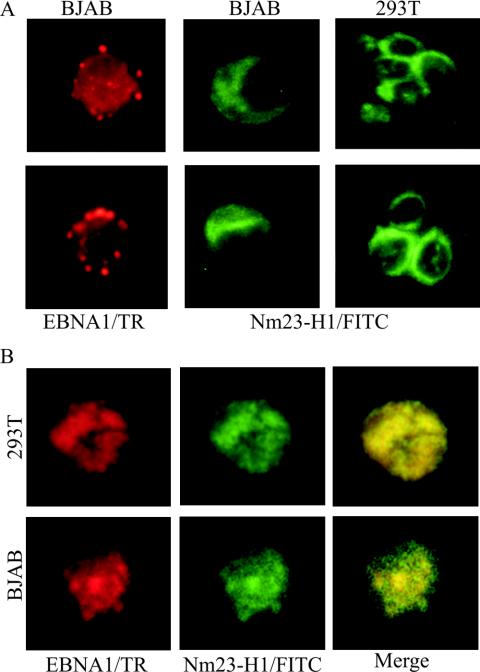
FIG. 4.
Immunofluorescence analysis of Nm23-H1 signals in transfected BJAB cells and in transfected 293T cells shows the specific signals for Nm23-H1 and EBNA1. (A) EBNA1 signals were detected in the nucleus with human serum adsorbed against human B-cell lines and were previously shown to have specific signals for EBNA1 by immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis. Signals were detected by using anti-human antibody-conjugated Texas Red antibody at 1:1,000 dilutions. Mouse monoclonal antibody to Nm23-H1 was used as primary antibody and goat anti-mouse fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated antibody was used at 1:150 and 1:2,500 dilutions. EBNA1 signals show localization to the nucleus. (B) Signal when both the NM23-H1 expression plasmid (pA3M-Nm23-H1) and the EBNA1 expression plasmid (pSG5-EBNA1) were transfected in 293T and BJAB cells. Signals were visualized as described above. Nm23-H1 was translocated to the nucleus in the presence of EBNA1, and colocalization was observed by using a triple filter showing localization of both signals in similar nuclear compartments.