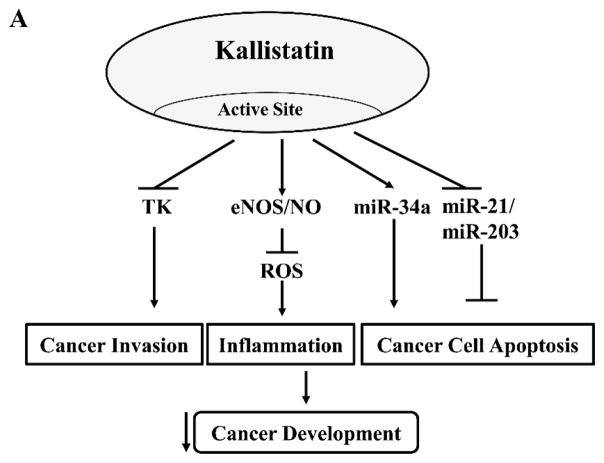
Figure 2.
Kallistatin’s active site and heparin-binding site play differential roles in blocking cancer development. (A). Kallistatin’s active site is key for modulating the effects induced by tissue kallikrein (TK), endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), nitric oxide (NO), miR-34a, miR-21 and miR-203. (B). Kallistatin’s heparin-binding site is essential for inhibiting the effects mediated by vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), epidermal growth factor (EGF) and Wnt.