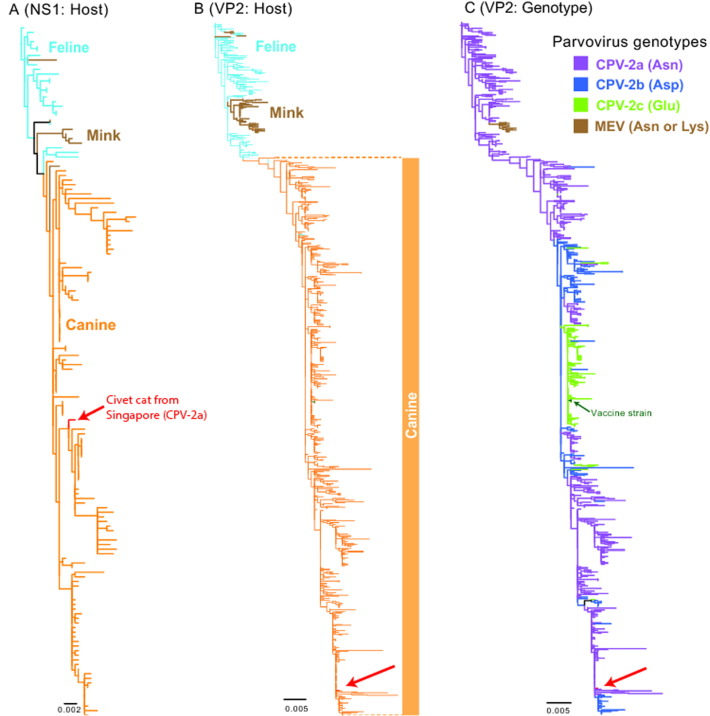
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic trees of parvovirus based on (A) non-structural (NS1) and (B) capsid (VP2) nucleotide sequences from various hosts: canine parvovirus (CPV), feline parvovirus (FPV) and mink enteritis virus (MEV). (A) Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogeny of 150 full-length NS1 sequences. Colored branches denote host species. (B) ML phylogeny of 804 full-length VP2 sequences. Color branches denote host species. Red arrow indicates CPV sequences of a civet cat from Singapore. (C). Colored branches of VP2 phylogeny represent different genotypes at an amino acid position 426: CPV-2a (Asn), CPV-2b (Asp) and CPV-2c (Glu). Green arrow indicates live attenuated CPV vaccine. Abbreviations: Asn, asparagine; Asp, aspartic acid; Glu, glutamic acid; Lys, lysine.