Figure 6.
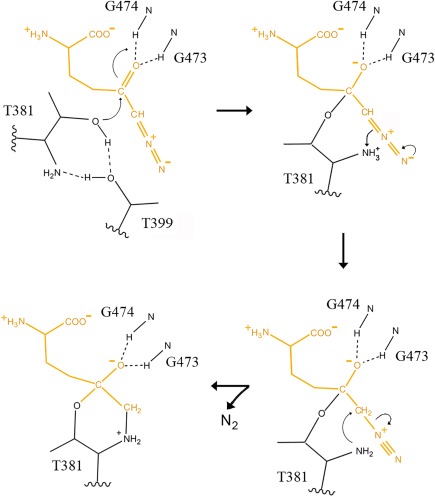
Proposed mechanism of hGGT1 inactivation by DON. The amine of Thr381 activates the nucleophile by accepting a proton from the OG oxygen of Thr381 via OG atom of Thr399. The OG atom of Thr381 attacks the carbonyl carbon (C5) of the DON molecule (top left structure). These results in the formation of a tetrahedral adduct which is stabilized by the interaction between the carboxy‐oxygen of DON and the main chain nitrogen atoms of Gly473 and Gly474 (top right structure). An electron pair on N7 of DON migrates to generate an N‐N triple bond and a proton is transferred from the amine of Thr381 to the C6 of DON (bottom right structure). Attack of the α‐nitrogen of Thr381 on the C6 of DON cleaves the single C‐N bond of the DON molecule releasing N2 and results in the formation of a covalent bond between the α‐nitrogen of Thr381 and C6 of DON. The final product (detected in the x‐ray structure, Figs. 3–5) contains a six‐membered ring composed of N, CA, CB, OG of the Thr381 and the C5 and C6 atoms of DON (bottom left structure).
