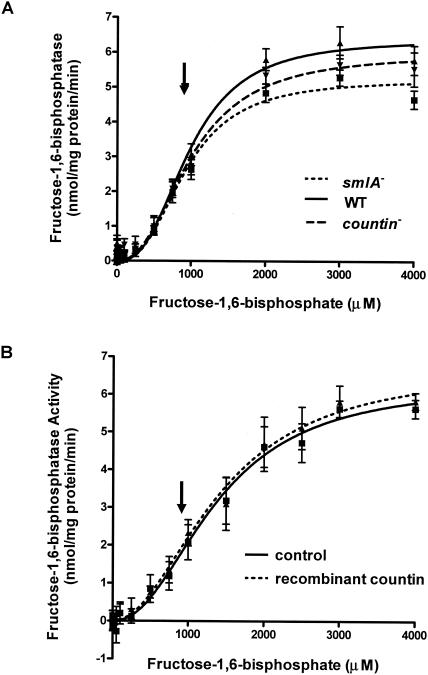
FIG. 5.
Activity of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase in cell lines with different extracellular CF activity. (A) smlA mutant, wild-type (WT), and countin mutant cells were starved by shaking in PBM and collected 6 h later. The activities of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase were measured by varying the concentration of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in the assay buffer and by coupling the reaction to the formation of NADPH. Values are means ± standard error of the mean from five independent assays. The lines show Hill equations fit to the data with nonlinear regression. For wild-type cells, the Vmax was 6.4 nmol/mg of protein/min, the Km was 980 μM, and the Hill coefficient was 2.7. (B) Wild-type cells were starved by shaking in PBM and harvested at 6 h of starvation. Cells were treated with 200 ng of bovine serum albumin per ml (control) or recombinant countin for 1 min and then collected. The activity of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase was measured as in panel A. Values are means ± standard error of the mean from five independent assays. The lines show Hill equations fit to the data with nonlinear regression. The arrows indicate the physiological level of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (≈914 μM).