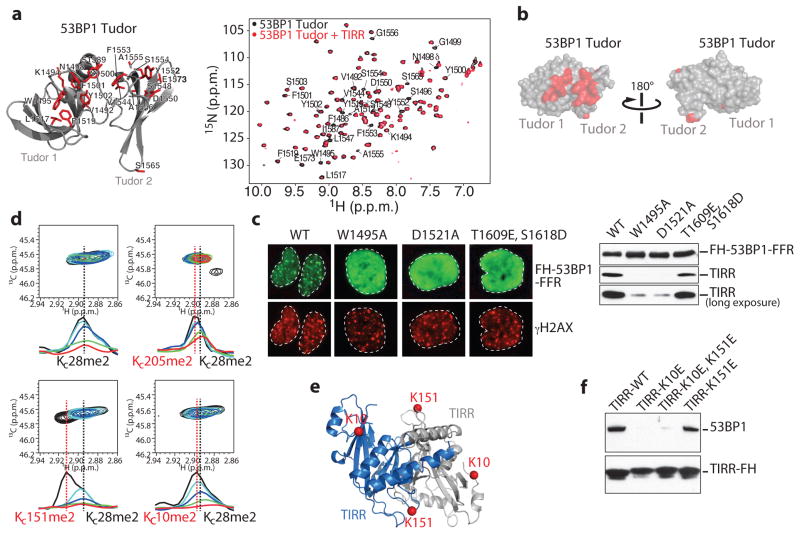
Figure 2. TIRR associates with the tandem Tudor domain of 53BP1.
a, (Left) Representation of 53BP1 Tudor (PDB, 2G3R) highlighting in red residues with preferential signal broadening in the 1H-15N HSQC spectrum of Tudor upon titration with unlabeled TIRR. (Right) Overlay of the 1H-15N HSQC Tudor spectra in the absence (black) and presence (red) of TIRR (Tudor:TIRR molar ratio of ~1:0.3). 53BP1 residues with preferential signal broadening are labeled. b, 53BP1 Tudor surface representation showing residues with preferential decrease in signal intensities (see a). c, Immunofluorescence (Left) and Flag immunoprecipitation (Right) using indicated cells. d, Overlay of 1H-13C HMQC spectra of 13C-labeled dimethylated lysine analogs in TIRR (KC10me2, KC28me2 KC151me2 and KC205me2) in the absence (black) and presence of unlabeled 53BP1 Tudor [TIRR:53BP1 molar ratios: 1:0.1 (cyan), 1:0.25 (blue), 1:0.5 (green), 1:1 (red)]. Also shown are 1D slices of the 1H-13C HMQC spectra in the 1H dimension highlighting the preferential broadening of KC10me2 and KC151me2 compared to KC28me2 and KC205me2. e, Residues K10 and K151 highlighted in TIRR crystal structure (PDB, 4ZG0). TIRR gene accession # is NC_000016.10. f, Flag immunoprecipitation from indicated U2OS extracts.