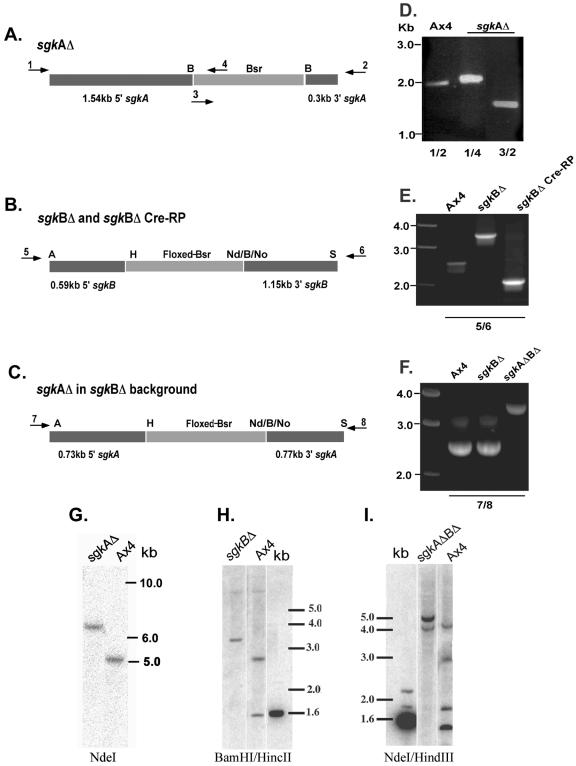
FIG. 2.
Construction and verification of sgk-null strains. (A to C) Schematic presentations of the construction vectors used for homologous disruption of the genes (not drawn to scale). Arrows represent the oligonucleotide primers used for verification of the gene disruptions by PCR. The PCR primers were outside the regions of the genes used for the construction vectors. Abbreviations: B, BamHI; H, HindIII; Nd, NdeI; No, NotI; S, SacII; A, ApaI. (D to F) PCR verification of gene disruptions. (G to I) Southern analyses of the sgk single and double mutants. sgkAΔ (A and D) primers 1 and 2 are sgkA-specific primers and yield the predicted 2-kb fragment from the AX4 parent strain. Primers 3 and 4 are Bsr-specific primers. Primer combinations 1 and 4 (1/4) and 3/2 generate the predicted 2.1- and 1.7-kb PCR products, respectively, from the sgkAΔ strain. (G) Southern analysis with an sgkA-specific probe confirms the insertion of a 1.4-kb cassette into the 5-kb sgkA NdeI fragment. sgkBΔ (B and E) primers 5 and 6 are sgkB-specific primers and generated the predicted 2.5-kb fragment from the Ax4 parent and a 3.4-kb fragment from the disrupted Bsr-containing gene. The cre recombinase product was verified with the same primers to generate a 2.0-kb PCR fragment(representing the loss of the Bsr cassette and part of the sgkB gene). (H) Southern analysis with the sgkB-specific probe confirms the disruption of the parental copy of the gene. sgkAΔBΔ (C and F) The disruption was verified by PCR with sgkA-specific primers 7 and 8, which generate a 2.5-kb fragment in the parental strain (Ax4) and in the sgkBΔ (where sgkA is unaffected) and a 3.3-kb fragment in the double mutant, where the Bsr cassette is inserted into the sgkA gene. (I) Southern analyses of the double mutant with an sgkA-specific probe confirms the disruption of the parental 5-kb NdeI fragment and the generation of 2.9-kb NdeI-HindIII, 1.7-kb NdeI, and 1.4-kb HindIII-NdeI fragments in the mutant strain.