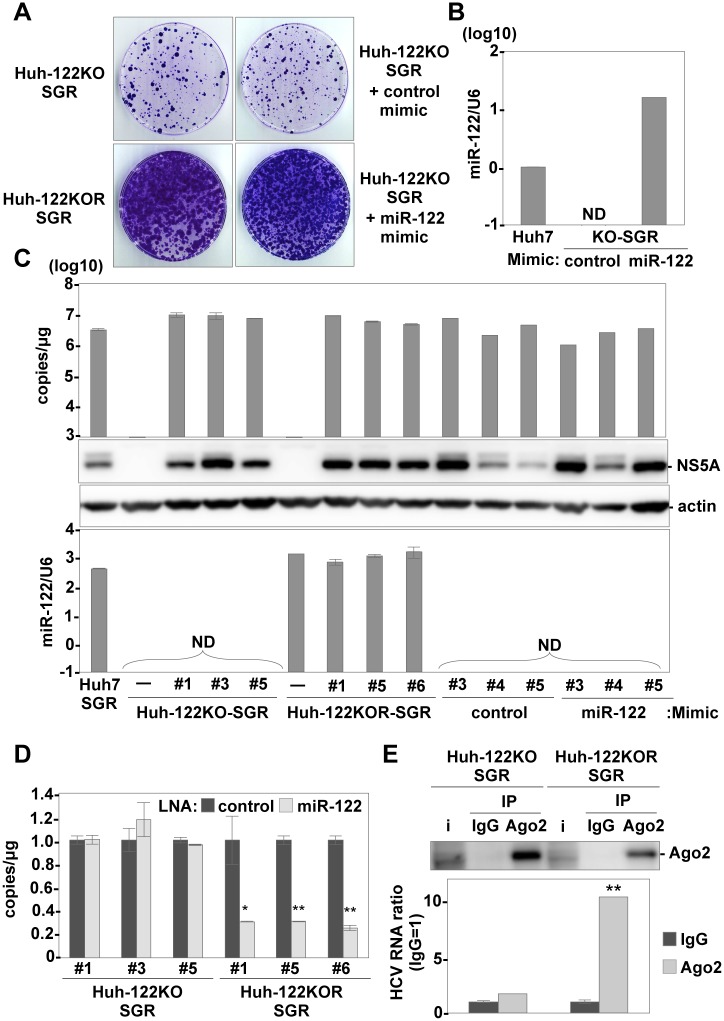
Fig 1. Establishment of replicon cells derived from Huh7-122KO cells.
(A) Subgenomic HCV replicon RNA was electroporated into Huh7-122KO and Huh7-122KOR cells, or into Huh7-122KO cells together with control- or miR-122-mimic, and G418-resistant colonies were stained with crystal violet at 21 days post-transduction. (B) Expression of miR-122 in Huh7-122KO cells electroporated with either control-mimic or miR-122-mimic at 72 h post-electroporation. Relative expression of miR-122 was determined by qRT-PCR by using U6 snRNA as an internal control. (C) Each of the three clones derived from each type of replicon cells was subjected to qRT-PCR after extraction of total RNA (top) and to immunoblotting by using anti-NS5A and β-actin (middle). The relative expression of miR-122 was determined by qRT-PCR by using U6 snRNA as an internal control (bottom). (D) Intracellular HCV-RNA replication in Huh7-122KO-SGR cells (#1, #3, #5) and Huh7-122KOR-SGR cells (#1, #5, #6) in the presence of 20 nM of either LNA-control or LNA-miR122 was determined by qRT-PCR. (E) The Ago2 complex was immunoprecipitated from Huh7-122KO-SGR#1 and Huh7-122KOR-SGR#1 cells by using either anti-IgG or anti-Ago2 mouse antibody. The HCV-RNA associated with Ago2 was determined by qRT-PCR and Ago2 was detected by immunoblotting. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean and asterisks indicate significant differences (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) versus the results for the control.