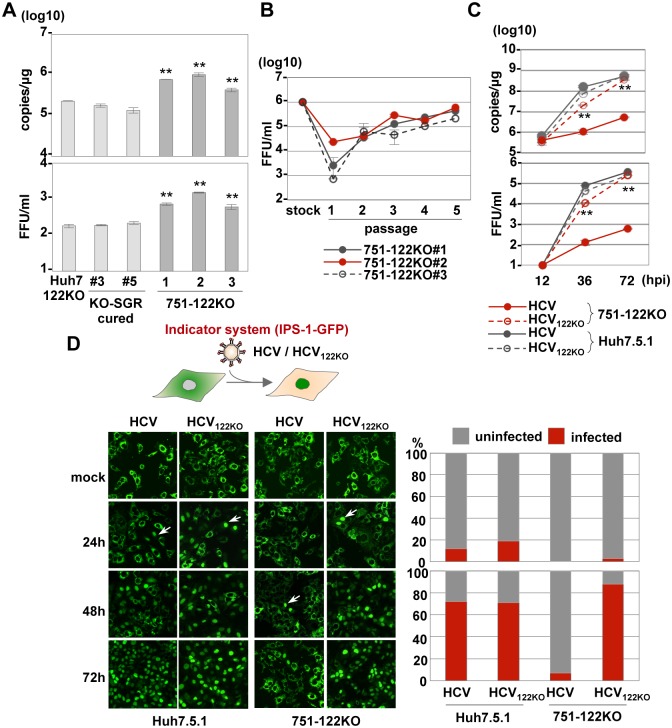
Fig 4. Propagation of HCV122KO in 751-122KO cells.
(A) HCV was inoculated into Huh7-122KO (#2), Huh7-122KO-cured (#3 or #5), or 751-122KO (#1, #2 or #3) cells, and the levels of intracellular HCV-RNA replication (top) and infectious titers in the culture supernatants (bottom) were determined by qRT-PCR and focus formation assay, respectively, at 72 hpi. (B) Infectious titer in the culture medium on serial passage of each 751-122KO cell clone. (C) HCV and HCV122KO were inoculated into 751-122KO and Huh7.5.1 cells and the levels of intracellular HCV-RNA replication (top) and infectious titers in the culture supernatants (bottom) were determined at 72 hpi. Error bars indicate the standard deviation of the mean and asterisks indicate significant differences (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) versus the results for the control. (D) Nuclear translocation of IPS-GFP (arrows) in Huh7.5.1 and 751-122KO cells upon infection with HCV and HCV122KO (left panels). The numbers of cells having translocated GFP in their nuclei through propagation of HCV were counted and the infection ratios at 24 hpi (right top) and 72 hpi (right bottom) were determined.