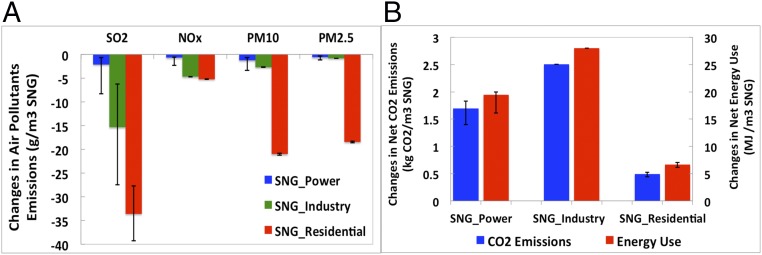
Fig. 2.
(A) Decreases in air pollutant (SO2, NOx, PM10, and PM2.5) emissions and (B) increases in CO2 emissions and energy consumption due to SNG substitution for coal. Vertical lines show the range of smallest to largest potential for changes in energy use and air pollutant and CO2 emissions due to the lower bound (SNG displaces cleanest coal first) and upper bound (SNG displaces dirtiest coal first) substitution scenarios described in Table S1. The industrial sector has no error bar for CO2 emissions and energy intensity due to the simplifying assumption in the ECLIPSE emission scenario that industrial coal boilers have the same CO2 EF and thermal efficiency (SI Materials and Methods, Estimating Air Pollutant and Carbon Dioxide Emission Changes and Table S2).