Fig. 5.
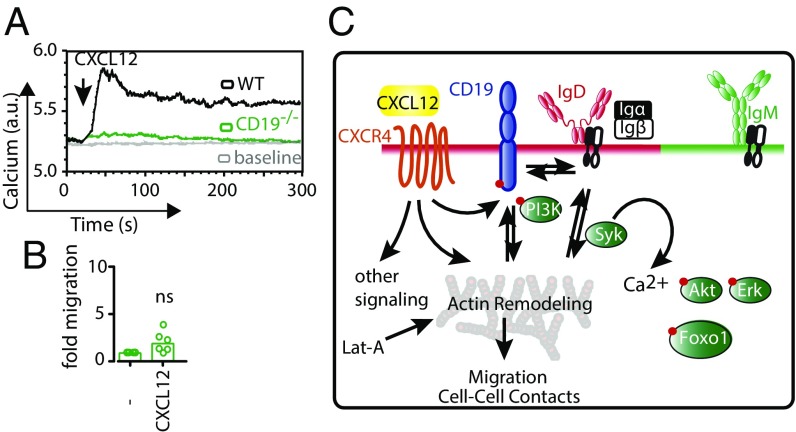
CD19 is the linchpin between CXCR4, the BCR, and the actin cytoskeleton. (A) Calcium flux measurement of WT (black) and CD19−/− (green) splenic B cells in response to 100 ng/mL CXCL12. (B) Migration of WT (black) and CD19−/− (green) splenic B cells toward CXCL12 over a period of 4 h. Calcium flux analyses in A and migration analysis in B are representative of four and six independent experiments, respectively. (C) Schematic representation shows plasma membrane localization of IgM and IgD on mature B cells and chemokine receptor CXCR4 that resides in the IgD–CD19 island. Upon engagement of CXCL12, CXCR4 triggers a multitude of signals including actin remodeling. As a result of actin remodeling, a Syk-dependent BCR signal, specifically through the IgD–BCR, is triggered, and a feedforward loop is initiated that induces Ca2+ influx, Akt/Foxo1 and Erk pathway activation in addition to F-actin reorganization. The later part of actin remodeling could also be initiated by cytoskeleton disruption using Lat-A, thus enabling the study of the effect of the chemokine-driven actin remodeling on the BCR.