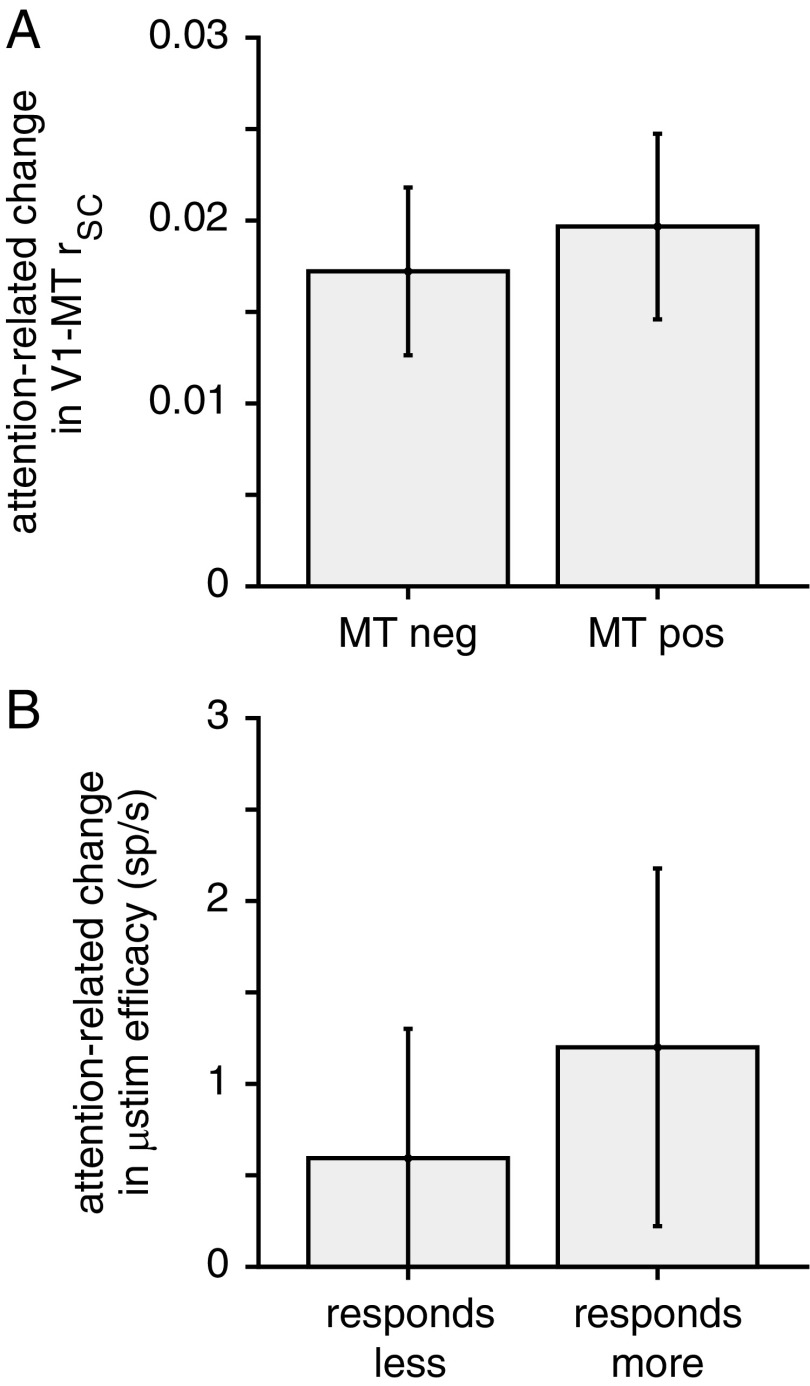
Fig. 7.
Correlative and causal evidence that the attention-related changes in the weighting between V1 and MT are not accomplished through changes within MT. (A) Median attention-related change in V1–MT rSC under conditions when attention is associated with decreases in the rate of an MT unit (Left) or increases in the rate of an MT unit (Right). Error bars represent SEM. (B) Median number of extra spikes elicited by V1 electrical microstimulation in MT units that respond less (Left) or more (Right) to the visual stimulus overlapping the receptive fields of the stimulated V1 units. Conventions as in A.