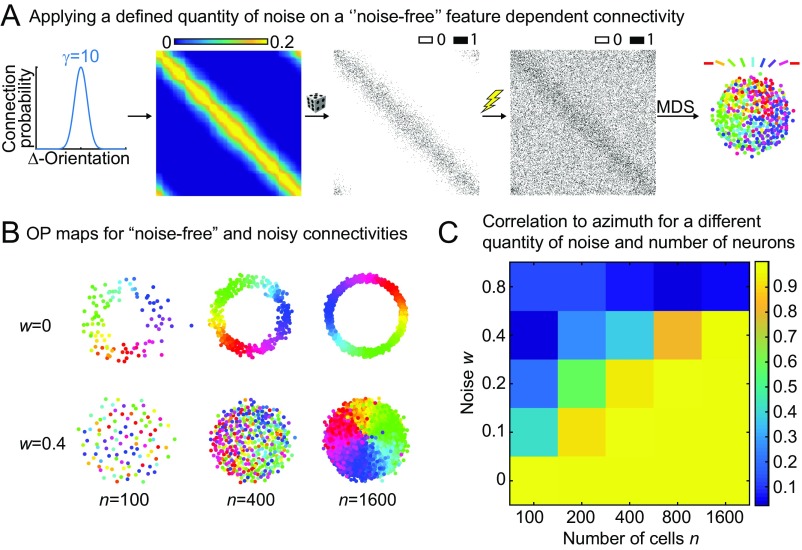
Fig. S2.
Influence of noise on the optimal placement of orientation-selective neurons. (A) A highly selective noise-free connection function is used (γ = 10) to generate a connection matrix that accordingly is also noise-free. Noise is then applied by randomly setting a bin in the connection matrix to either zero or one, where the probability to change a bin is given by the noise parameter w. (B) OP maps for noise-free and noisy connectivities (w = 0.4). (C) Correlation to azimuth for more extensive parameter values of n and w. The constants a and b were set to 0 and 0.2, respectively, for all of the shown calculations.