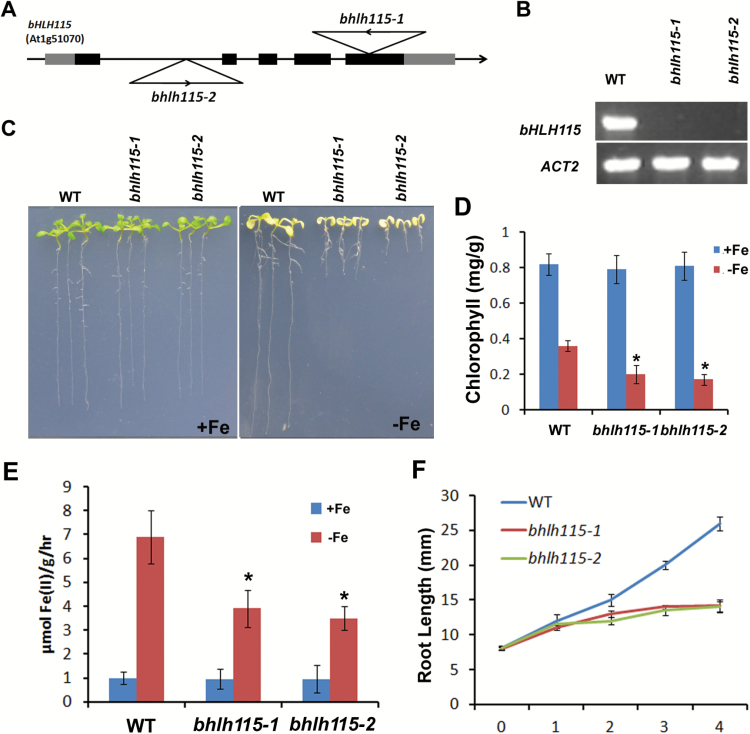
Fig. 1.
Characterization of bhlh115 mutants. (A) Location of T-DNA in the bHLH115 gene. Thick bars and lines indicate the exons and introns, respectively. Grey bars indicate the 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions. Triangles indicate the location of the T-DNA. (B) Confirmation of the bhlh115-1 and bhlh115-2 mutants. The full-length cDNA of bHLH115 was amplified by RT-PCR. (C)Images of 10-d-old seedlings that were germinated directly on +Fe or –Fe media. (D) Chlorophyll content of leaves on +Fe or –Fe media. Significant differences from the wild-type were determined by Student’s t-test, *P<0.05). (E) Iron reductase activity. Seedlings were germinated and grown on +Fe medium for 10 d and then transferred to –Fe media for 3 d. Significant differences from the wild-type were determined by Student’s t-test, *P<0.05). (F) Time-course quantification of root length of plants from 0 to 4 d after transfer to –Fe medium.