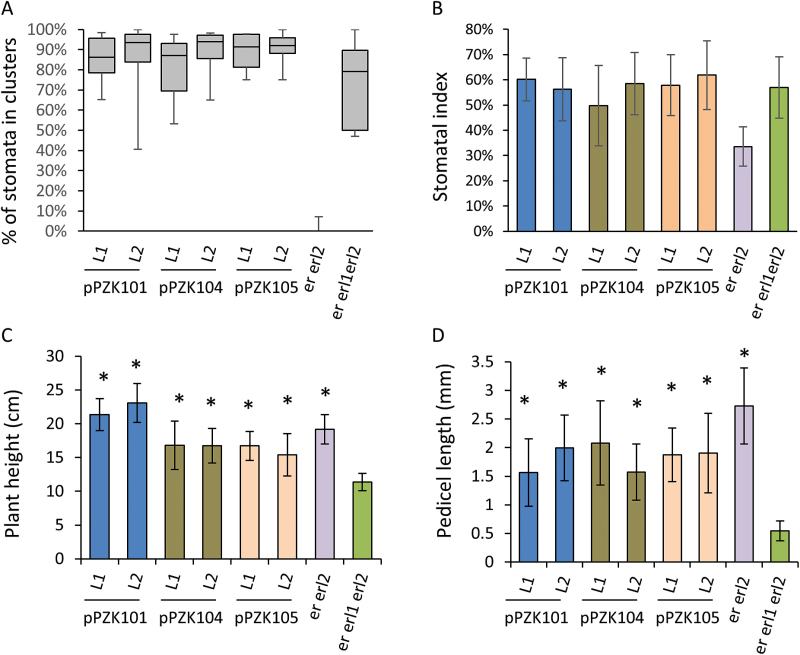
Fig. 6.
While substitution of the conserved lysine residue (K676E) in the ATP binding site of the ERECTA kinase domain (pPZK101) or deletion of short JMD segments (pPZK104 and pPZK105) disrupt ability of ERECTA to rescue stomatal phenotypes of er erl1 erl2, those constructs partially rescue elongation of above-ground organs. Constructs were transformed into er erl1/+ erl2 mutants and two independent transgenic lines in the er erl1 erl2 background were analyzed in the T3 generation. In (A) the median is indicated as a thick horizontal line, upper and lower quartiles are represented by the top and the bottom of the boxes, and the vertical lines designate the maximum and the minimum. (A, B) Epidermal phenotypes were analyzed on the abaxial side of 17-d-old cotyledons (n=8–16). (B–D) Values are means ± SD. (C) Height of mature plants (n=12–21). (D). Lengths of mature pedicels on the main stem (n=80; eight measurements per stem). (C, D) Values significantly different from er erl1 erl2 (P<0.00001) are indicated by asterisks.