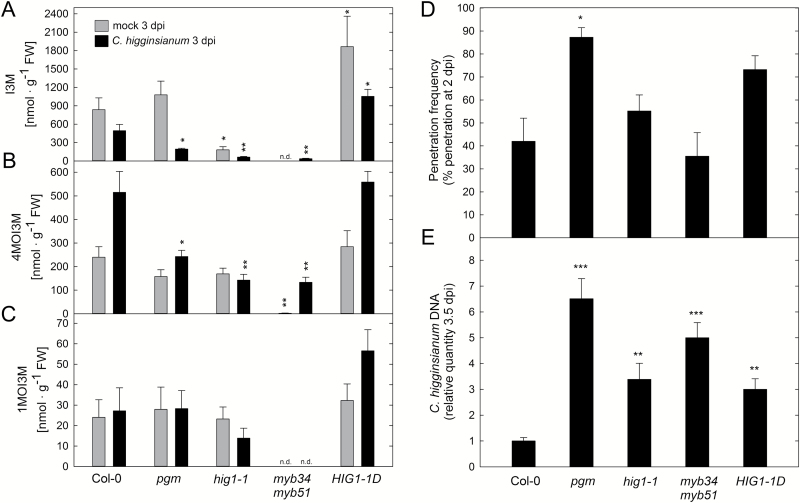
Fig. 3.
Analysis of indolic glucosinolate relevance in resistance to C. higginsianum. Indolic glucosinolate content was determined in 5-week-old leaves of Col-0, pgm, hig1-1, myb34 myb51, and HIG1-1D 3 dpi with C. higginsianum and mock treatment. (A–C) Indole-3-ylmethyl-glucosinolate (I3M; A), 4-methoxy-indole-3-ylmethyl-glucosinolate (4MOI3M; B), and 1-methoxy-indole-3-ylmethyl-glucosinolate (1MOI3M; C) contents were quantified in four biological replicates ±SE. (D) Penetration frequency as measured by the percentage of successful penetration events at 2 dpi. Values are means of three biological replicates ±SE. Per replicate, the penetration success of 200–300 appressoria on two leaves was scored. (E) The relative quantity of genomic C. higginsianum DNA in leaf samples was determined by qPCR at 3.5 d post-infection. Values are means of three biological replicates measured in three technical replicates ±SE. For each replicate, fully expanded leaves of two infected plants were pooled. Asterisks indicate a significant difference to Col-0 (*P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; Student’s t-test). n.d.: not detectable.