Figure 10. Canine BEST1-associated maculopathy is a disease of an RPE-photoreceptor interface.
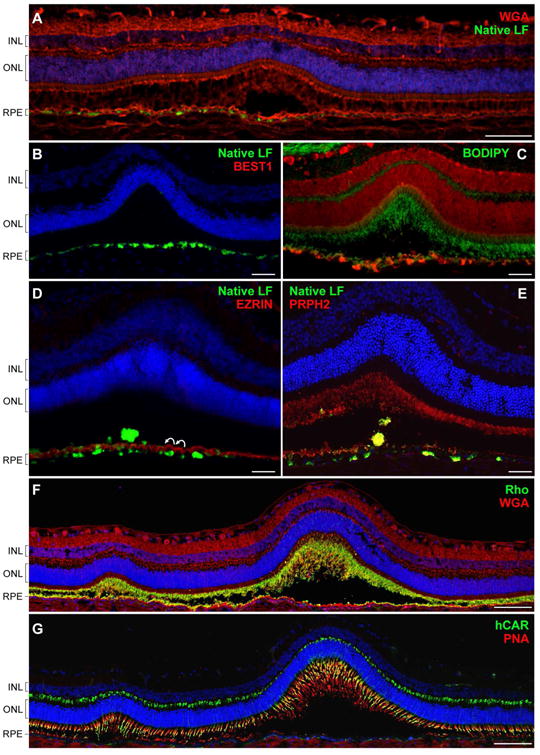
(A) Confocal photomicrograph of an early pre-vitelliform lesion. The section was stained with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA, red) and DAPI (blue). Bright green fluorescent signals of lipofuscin granules (native LF) were found to be associated with RPE cells directly underlying the primary neuroretinal disruption as well as its immediate surrounding areas. (B) Cryosection from a 30-month-old cBest1-R25X-affected dog with more advanced subretinal lesions comparable to stage II (vitelliform) in BVMD. BEST1-deficient RPE cells accumulate fluorescent debris subjacent the serous retinal detachment. (C) Retinal cross-section through an early vitelliform lesion from a 25-month-old dog harboring premature stop mutation (R25X) in the canine BEST1. The section was pretreated with ethanol before applying BODIPY 493/503 (green) and propidium iodide (red) for nuclear counterstaining. An evident increase of EC-BODIPY was recorded within the detached and more intact areas adjoining to the lesion. (D) Advanced vitelliform lesion immunolabeled with anti-EZRIN (red) and stained with DAPI (blue). Note the striking undulation of the RPE apical membrane (white curved arrows), absence of EZRIN-positive RPE apical projections, and beginning of a buildup of autofluorescent debris in the subretinal space (native LF fluorescence). (E) Similar cBest lesion in a 25-month-old cBest1-R25X-affected dog labeled with anti-PRPH2 (red). Peripherin-stained photoreceptor debris occupy RPE apical surface delimiting its scalloped nature and RPE cell hypertrophy after the serous neuroretinal detachment. Cellular debris appear as yellowish subretinal aggregates. (F, G) Montage confocal photomicrographs of a large subretinal lesion and a satellite microlesion in vitelliform stage labeled with WGA (red) and anti-Rhodopsin (Rho, green) (F) or a combination of peanut agglutinin lectin (PNA, red) and anti-cone arrestin (hCAR, green) (G). Both the Rho- and hCAR-positive cellular debris were detected in the subretinal space of the mutant retinae. Nuclei were counterstained with propidium iodide (C) or DAPI, respectively. INL: inner nuclear layer; ONL: outer nuclear layer; RPE: retinal pigment epithelium. Scale bars: 100µm (A, F, and G), and 40µm applies to (B-E) panels.
