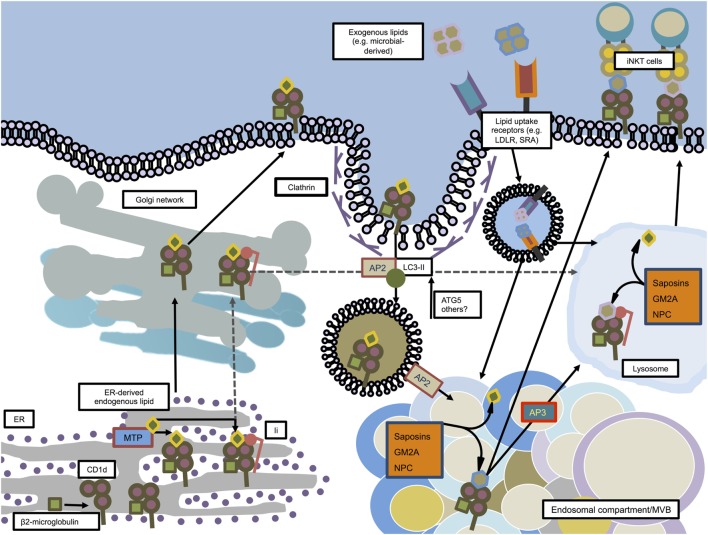
Figure 2.
CD1d trafficking and loading in mouse dendritic cells. CD1d molecules are synthesized in the ER where they associate with β2-microglobulin. Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) facilitates loading of ER-derived endogenous lipids onto CD1d in order to stabilize the molecule for further transport. In an independent pathway, some CD1d molecules associate in the ER with invariant chain (Ii). The Ii/CD1d complexes, after traveling through the trans-Golgi network, are directly guided to the lysosome. The non-Ii-associated CD1d molecules also pass the trans-Golgi network on their way to the plasma membrane. From there, facilitated by AP2 and members of the autophagy machinery, CD1d is internalized by clathrin-mediated endocytosis and guided toward endosomal compartments, where saposins, GM2 ganglioside activator (GM2A), and Niemann–Pick type C1 and C2 proteins (NPC1, NPC2) help exchanging endogenous lipids with exogenous or other endogenous lipids. From there, loaded CD1d may either be transported to the lysosome in an adaptor protein 3 (AP3)-dependent manner, or directly transported to the plasma membrane in order to interact with iNKT cells.