Figure 2.
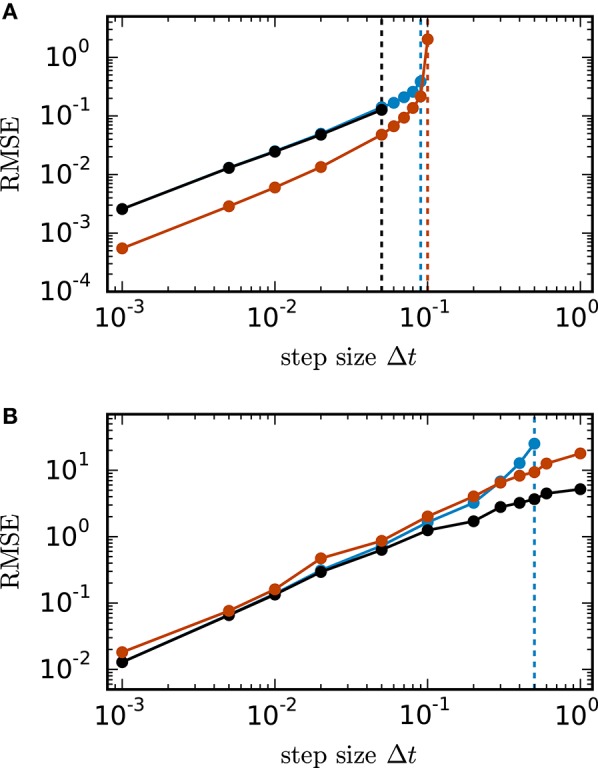
Accuracy of numerical methods for two networks of linear rate units. of the solution X obtained by the approximate solvers (blue curve: Euler-Maruyama method, black curve: implicit Euler method solved with fixed-point iteration, red curve: scalar exponential Euler method) with respect to the reference solution as a function of step size in double logarithmic representation. The respectively colored vertical lines mark the largest tested step size for which the corresponding methods deliver a solution with RMSE ≤ 1010. RMSE computed over 200.0 ms of biological time. (A) Inhibitory all-to-all test case. Network parameters: N = 400, μ = 0, σ = 10 and τ = 1 ms. (B) Sparse balanced e/i test case. Network parameters: N = 400, p = 0.2, μ = 0, σ = 10 and τ = 0.5 ms.
