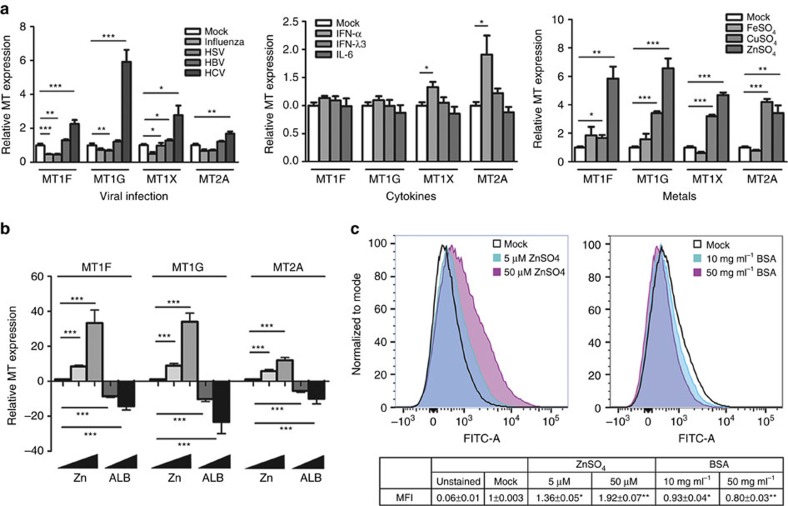
Figure 1. Metallothionein transcription is driven by diverse stimuli.
(a) To examine metallothionein induction, Huh-7 cells were either virally infected, or treated with cytokines or heavy metals for 8 h. Influenza and HSV downregulated metallothionein expression whereas HBV had little effect and HCV significantly upregulated all metallothioneins. None of the cytokines examined modulated MT1F and MT1G, and only IFN-α was able to induce MT1X and MT2A. Of the metal treatments, 50 μM ZnSO4 most potently upregulated all the metallothioneins, followed by CuSO4, while FeSO4 had little effect (Welch's t-test). (b) Huh-7 cells treated with zinc in low serum media showed a stronger induction of metallothioneins, confirming the zinc quenching role of albumin (Welch's t-test). In agreement, metallothionein expression was dose-responsively reduced with BSA treatment. (c) Quantification of intracellular zinc by Zinpyr-1 staining confirmed that zinc and albumin dose-dependently increase and decrease intracellular zinc, respectively (Welch's t-test). Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, (mean±s.e.).