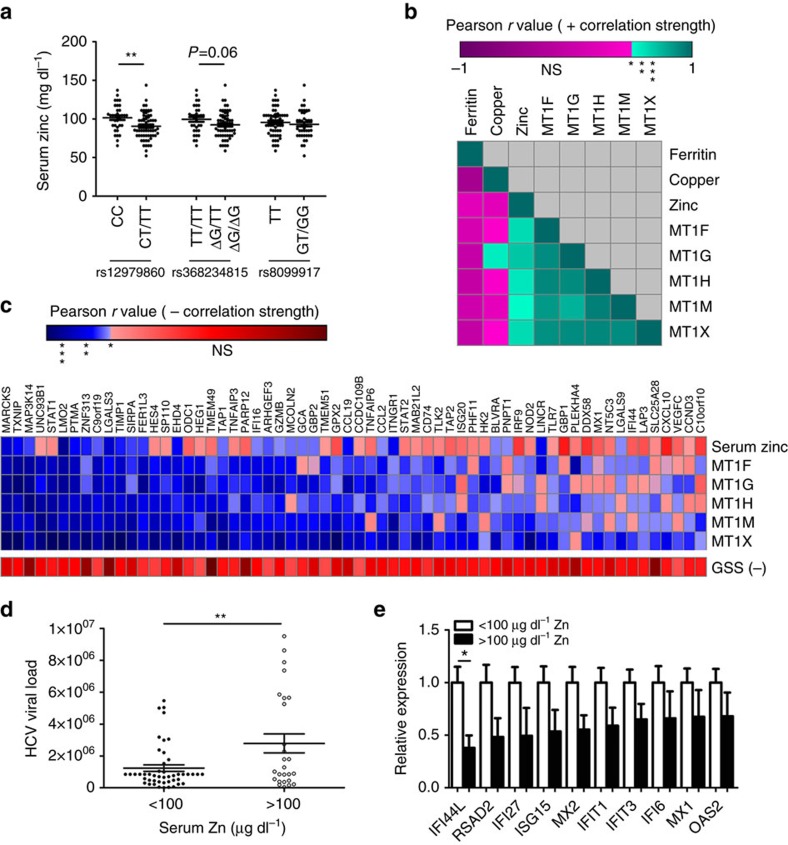
Figure 4. rs12979860 CC genotype increases serum zinc whilst inhibiting hepatic ISG expression.
(a) Significantly higher serum zinc levels were measured in chronic HCV patients that are carriers of the IFNL rs12979860 CC (major) genotype (Student's t-test). (b) Serum zinc was matched to microarray expression data, and was found to significantly correlate with hepatic metallothioneins, while both serum copper and ferritin did not show any strong relationship (Pearson correlation). (c) Serum zinc and metallothionein expression demonstrated a strong inverse correlation with hepatic ISGs (blue—significant inverse correlation, red—NS), suggesting that zinc can inhibit ISG expression in the liver (Pearson correlation). (d) HCV-infected patients were categorized into low (<100 μg dl−1) and high (>100 μg dl−1) serum zinc groups, with the high zinc group possessing significantly higher viral loads (Welch's t-test). Anti-HCV ISG expression was lower in the high zinc group (e), suggesting that zinc inhibits hepatic ISG expression resulting in increased viral replication and viral load (Welch's t-test). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, (mean±s.e.). NS, not significant; GSS, glutathione synthetase.