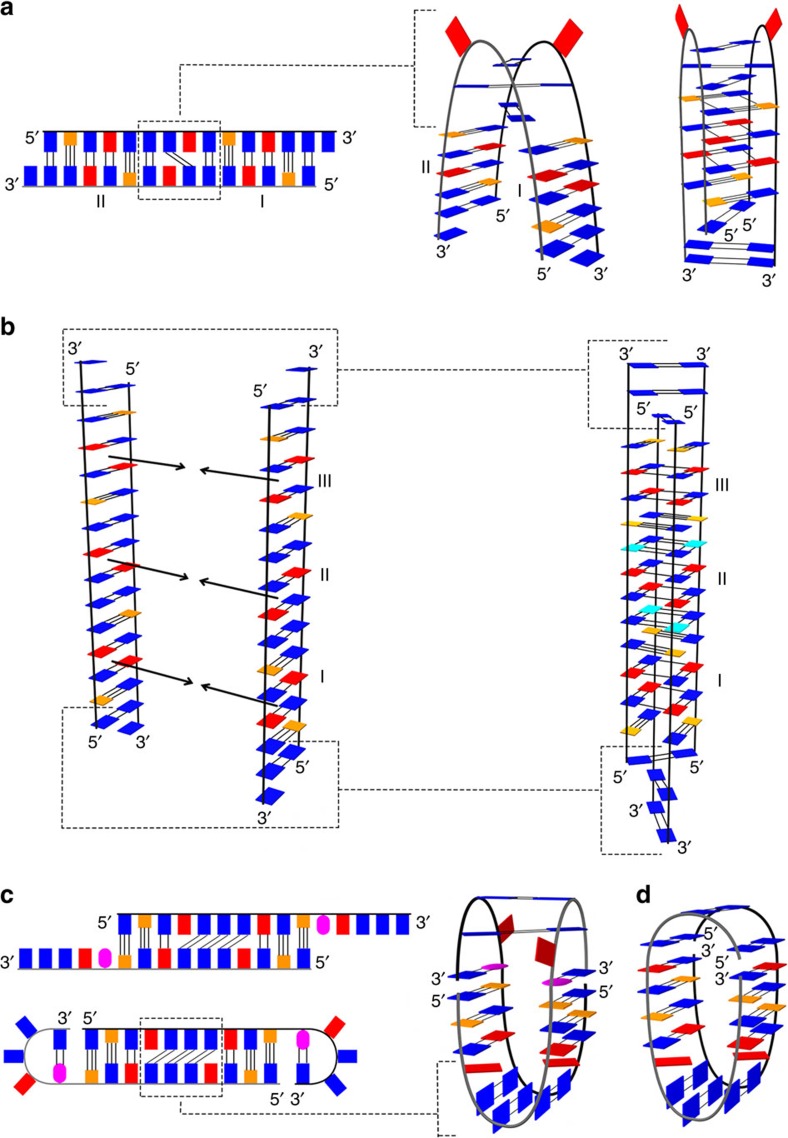
Figure 6. Simplified folding model of oligonucleotides with AGCGA repeats separated by GGG tracts.
(a) Folding model of the VK34 dimer. Roman numerals I and II indicate G-A base pairs that form the GAGA-core of the VK34 dimer. Completely folded VK34 dimer is shown on the right. (b) Folding model of the VK34 tetramer. The dashed lines show residues that form different base pairs in the VK34 tetramer than in the slipped duplex. Roman numerals I, II and III together with the arrows indicate G-A base pairs that associate into GAGA-quartets. (c) Folding model of VK34_I11. The dashed lines highlight different arrangements of two unpaired A4 residues separated by three G-G base pairs observed in a duplex compared with the VK34_I11 structure (right). (d) Topology of VK1. The guanine bases are shown in blue, guanines in syn conformation are indicated in cyan, inosine in magenta, adenine in red and cytosine in orange.