FIG 2 .
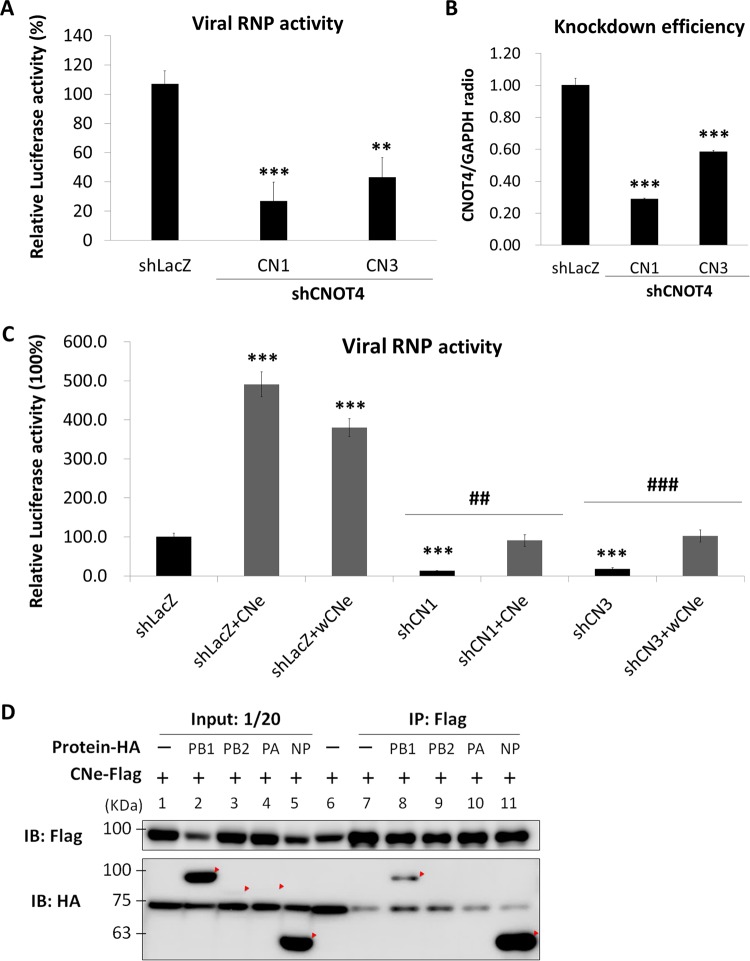
Viral RNP activity is correlated with the expression level of CNOT4. (A) Minireplicon assay results for RNP activity in CNOT4 knockdown cells. Two shCNOT4 clones, CN1 and CN3, and control shLacZ 293T cells were transfected with the plasmids for expression of viral PB1, PB2, PA, and NP and a reporter plasmid expressing the antisense luciferase gene as described elsewhere for the minireplicon assay (29). At 24 h posttransfection, luciferase activity was determined and normalized to the response of control shLacZ (means ± SD, n = 3). **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001, by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. (B) CNOT4 knockdown efficiency in 293T cells. (C) Overexpression of CNOT4 enhances viral RNP activity. CNOT4 knockdown (shRNA clones CN1 and CN3) or control cells (shLacZ) were transfected together with wild-type CNOT4 isoform e (CNe) or its wobble mutant (wCNe) and used for the minireplicon assay. Relative luciferase activities were measured as described for panel A (means ± SD, n = 3). ***, P < 0.001 (versus shLacZ); ##, P < 0.01; ###, P < 0.001 (versus shRNA clones CN1 or CN3), based on a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. (D) Interaction of CNOT4 with viral RNP components in an immunoprecipitation (IP) assay. 293T cells were cotransfected with Flag-tagged CNOT4 isoform e (CNe-Flag) and one of the HA-tagged viral proteins (PB1, PB2, PA, and NP). At 48 h posttransfection, cell lysates were precipitated using Flag-agarose. The proteins were visualized by Western blotting (IB) with anti-HA and anti-Flag antibodies.