Fig. 2.
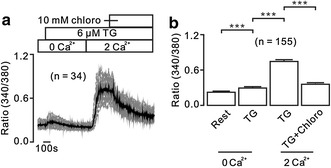
Chloro inhibits extracellular Ca2+ influx. a TG induced small transient increases of Ca2+ under Ca2+-free conditions (0 mM Ca2+ and 0.5 mM EGTA). Following the restoration of 2 mM Ca2+, large sustained elevations occurred and were declined by chloro. b The average Ca2+ levels from 155 cells. ***p < 0.001. These results indicate that chloro inhibits extracellular Ca2+ influx
