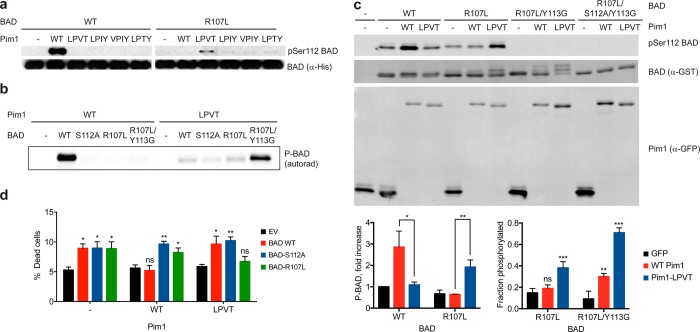
Figure 3.
Compensating mutation of the Pim1 substrate BAD producing a functional orthogonal kinase–substrate pair. (A) Phosphorylation of purified recombinant BAD (equal amounts of WT or R107L) in vitro with Pim1 (WT and quadruple mutants) was assessed by immunoblotting with a phospho-specific antibody against the primary Pim1 phosphorylation site (Ser112). (B) Phosphorylation of recombinant BAD (2 μM of WT or the indicated mutant) by WT Pim1 or Pim1-LPVT (100 nM) was assessed by radiolabel incorporation from [γ-33P]ATP. (C) Phosphorylation of BAD coexpressed with Pim1 in cultured cells. HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with the indicated Pim1 and BAD constructs, and expression levels and BAD phosphorylation were determined by immunoblotting. Bar graphs show mean ± SD (n = 3). For the chart on the left, statistical significance for the indicated differences was calculated by unpaired Student’s t test. For the chart on the right, statistical comparisons were made using a one-way ANOVA, followed by a Fisher’s LSD posthoc test comparing conditions to GFP control. For both charts, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.0001; ns, not significant. (D) Mutant Pim1 specifically rescues cells expressing BAD-R017L from apoptosis. Viability of COS7 cells stably transduced with a doxycycline-inducible Pim1-GFP construct (WT, LPVT mutant or empty vector [EV] control) following transfection with the indicated BAD expression constructs, induction of Pim1 expression, and serum starvation for 24 h was assessed by trypan blue staining. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 4 for EV, n = 7 for all others). Statistical comparisons for each group were performed as for the right chart in panel C, comparing each condition to EV.