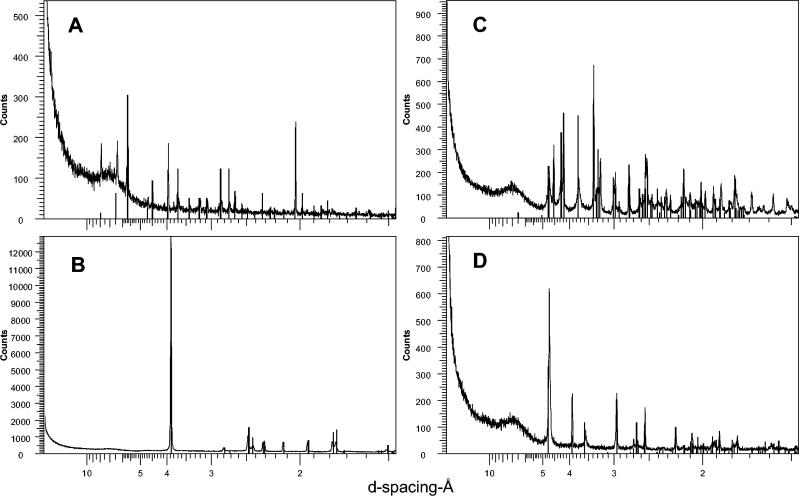
FIG. 5.
Typical XRPD patterns for metal oxalate crystals precipitated by B. caledonica in agar media or in the mycelium. (A) Cadmium oxalate formed on medium containing cadmium phosphate; (B) copper oxalate hydrate (moolooite) formed on medium containing copper phosphate or cuprite; (C) lead oxalate formed on medium containing lead phosphate, lead tetraoxide, lead sulfide, lead carbonate, and pyromorphite; (D) zinc oxalate dihydrate formed on medium containing zinc phosphate. The vertical bars indicate the peak positions and relative intensities for standard XRPD patterns of metal oxalates as given in the International Centre for Diffraction Data powder diffraction file. The standards used were cadmium oxalate (PDF-14-0712), copper oxalate hydrate (PDF-21-0297), lead oxalate (PDF-14-0803), and zinc oxalate dihydrate (PDF-25-1029). Typical spectra are shown from one of several plots.