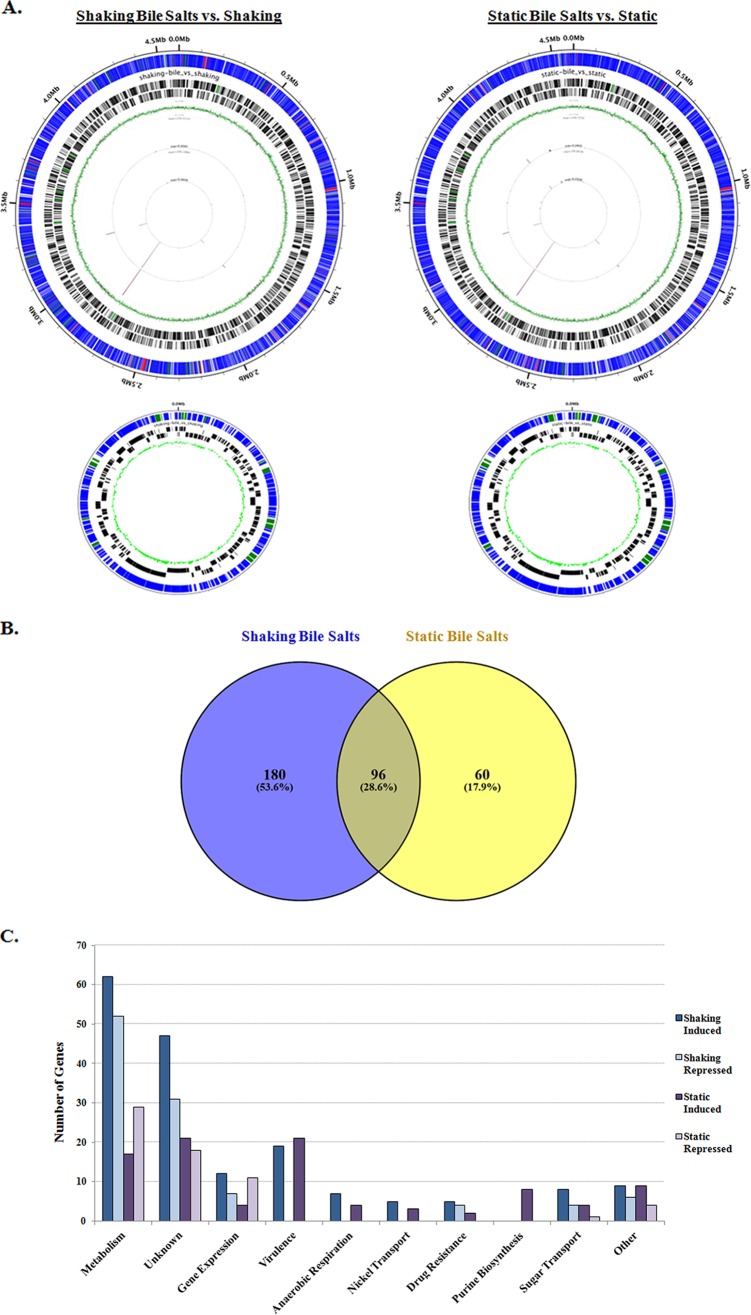
FIG 6.
RNA-sequencing analysis of S. flexneri 2457T grown in the presence and absence of 0.4% (wt/vol) bile salts. (A) Results of the RNA-seq analysis visualized with the Circleator program (71), in which blue represents unchanged genes, green represents induced genes (fold change ≥ 2, P < 0.05), and red represents repressed genes (fold change ≤ −2, P < 0.05) in the presence of bile salts for both the chromosome (top) and virulence plasmid (bottom). Barcodes represent forward and reverse genes, while the green circle represents the percent GC skew throughout the genome. (B) Venn diagram (72) of differentially expressed genes identified in the RNA-seq analysis. The numbers of induced and repressed genes for the “shaking + bile salts versus shaking” condition compared to the “static + bile salts versus static” condition are depicted. For both comparisons, there were 96 genes that were induced or repressed in the presence of bile salts. For the “shaking + bile salts versus shaking” analysis, there were an additional 180 genes induced or repressed, for a total of 276 differentially expressed genes in bile salts. For the “static + bile salts versus static” analysis, there were an additional 60 genes that were induced or repressed, for a total of 156 differentially expressed genes in bile salts. (C) Functional categories for differentially expressed genes in the presence of bile salts are plotted with the number of genes induced or repressed under the bile salts condition for both the shaking and static growth conditions. Please refer to Tables S2 and S3 in the supplemental material for details.