FIG 1.
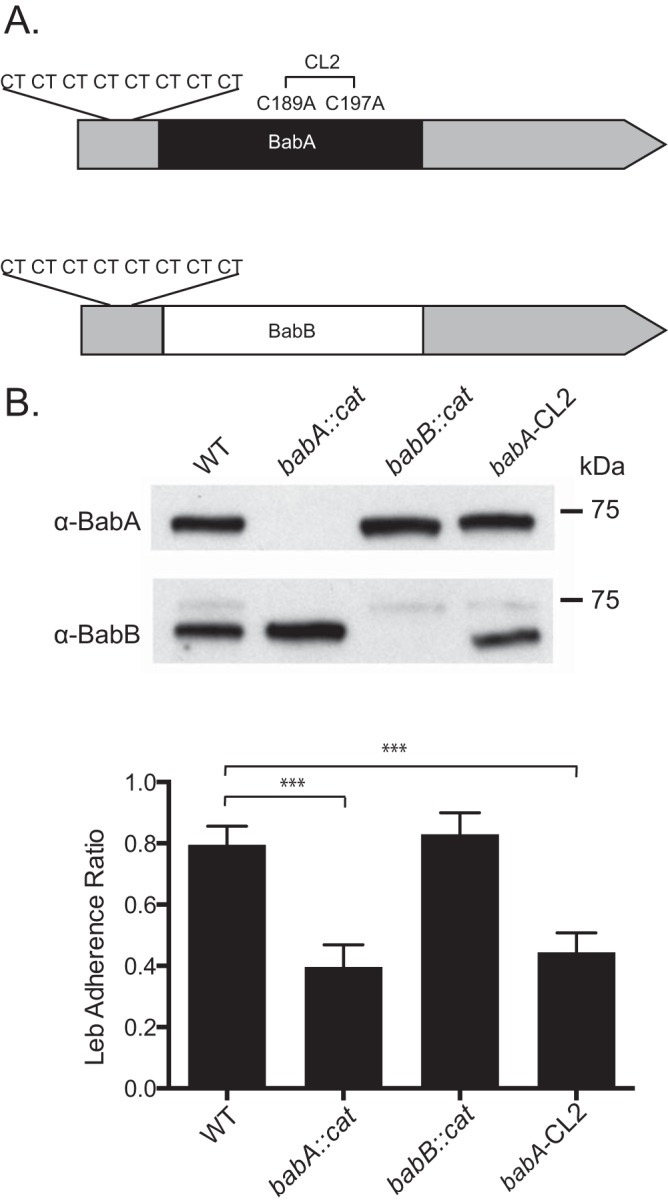
Characterization of WT H. pylori J166 and isogenic mutants. (A) babA and babB differ predominantly in the midregion of the genes, where BabA (black) binds Leb but BabB (white) does not, but are very similar at the 5′ and 3′ ends (gray). Both babA and babB have a series of eight CT repeats at the 5′ end that is in frame. Cys189 and Cys197 in babA form a redox-sensitive disulfide-clasped loop designated CL2, which is essential for Leb binding. Modification of Cys to Ala at residues 189 and 197 (babA-CL2 mutant) eliminates Leb binding. (B) Immunoblotting of WT H. pylori J166, the babA-CL2 mutant, and isogenic strains with deletions of babA (babA::cat mutant) and babB (babB::cat mutant). The faint band obtained with the anti-BabB antibody is cross-reactivity with BabA, and it is not seen in the babA::cat mutant. ELISA (bottom) demonstrates that the WT and the babB::cat mutant attach to Leb but the babA::cat and babA-CL2 mutants do not. ***, P < 0.001.
