FIG 5.
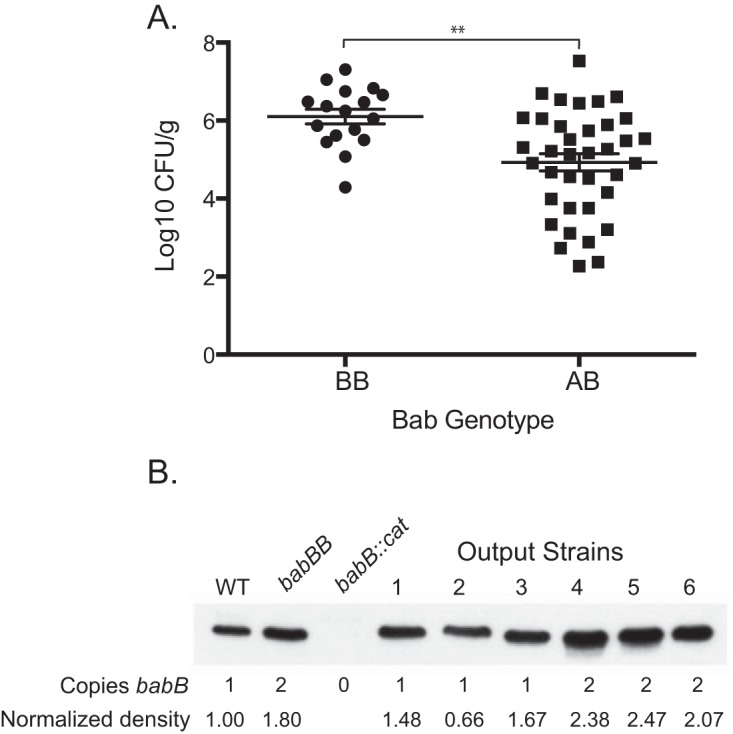
Overexpression of BabB enhances H. pylori fitness in rhesus macaques. (A) The Bab genotype at the babA locus was determined for an average of 10.6 (SD = 3.2) colonies recovered from monkeys challenged with the WT, the babA::cat mutant, or the babA-CL2 mutant and biopsied 2 to 20 weeks p.i. The genotype was defined as BB when >50% of the colonies contained two copies of babB and AB when ≥50% contained one copy each of babA and babB. When the results were collapsed over time, animals colonized predominantly with strains that duplicated babB (BB) showed approximately 10-fold greater bacterial loads (**, P = 0.001). Animals without detectable colonization were excluded. (B) Immunoblotting with BabB antiserum of H. pylori J166 (WT with one copy of babB), the babBB mutant (engineered to have two copies of babB), the babB::cat mutant, and rhesus output strains having one or two copies of babB. Immunoblotting and densitometry normalized to the total protein (see Materials and Methods) demonstrated that strains with duplicated babB express approximately 2× BabB protein.
