FIG 4.
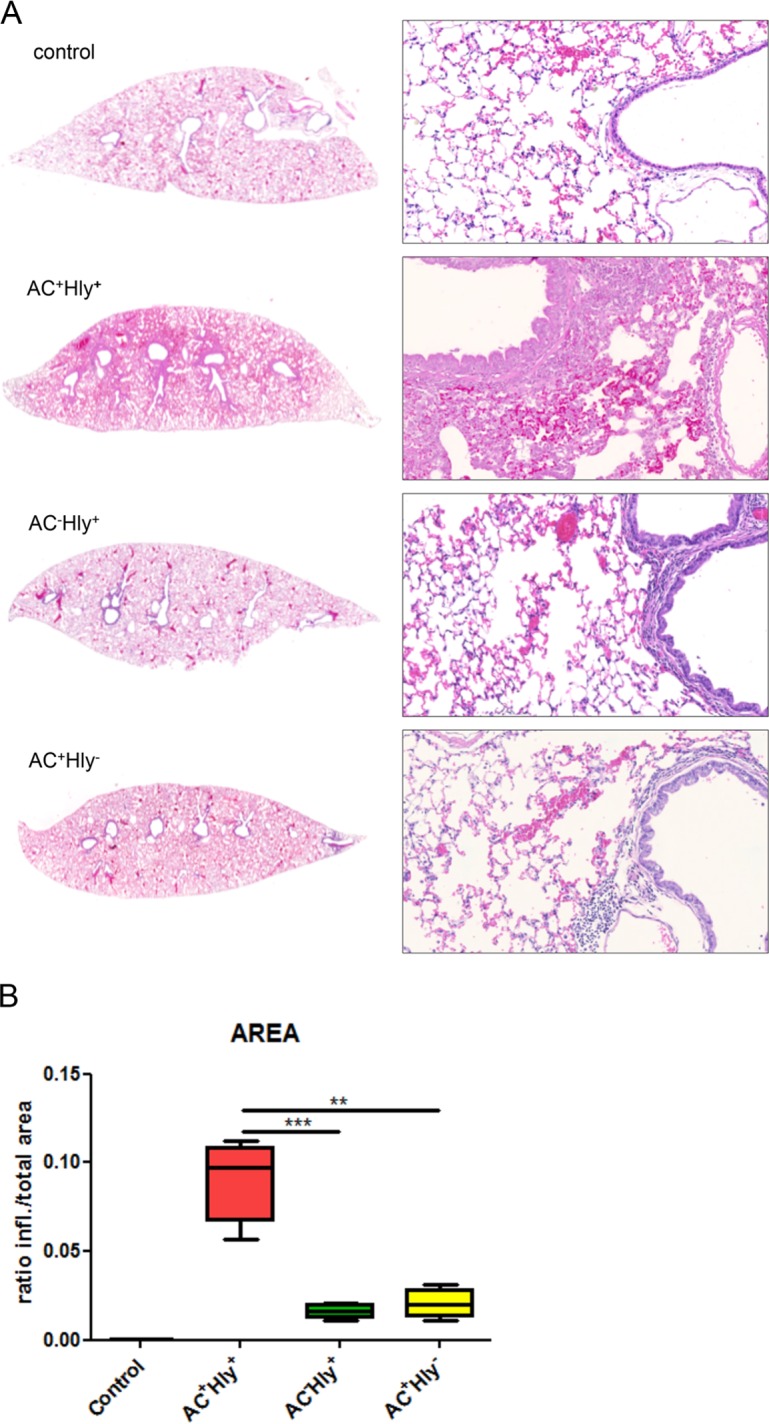
The B. pertussis AC+ Hly− mutant elicits significantly milder inflammation of infected lungs than the parental strain. Four BALB/c mice per group were infected intranasally with 1.5 × 105 CFU in 50 μl of suspensions of the indicated B. pertussis strains. The animals were sacrificed on day 6, and lungs were processed for staining with hematoxylin and eosin (see Materials and Methods for details) and scanned. Control mice received SS medium only. (A) Longitudinal sections of the left lobes at the original magnification of 1,25× that are representative of 3 serial sections per lung lobe. The right panels show enlargements of representative images of the bronchi and peribronchial parenchyma at magnification 20×. Lungs of animals infected by the AC+ Hly+ strain exhibited bronchopneumonia affecting the regions primarily around the large lobar bronchi. Significantly milder inflammation is observed in the lungs of animals infected by the AC+ Hly− and AC− Hly+ strains. (B) Inflamed parenchyma regions were manually delimited on three consecutive lung sections for 4 infected animals per group (12 sections analyzed in total) and scanned using an AxioScan.Z1 automated slide scanner, and the ratios of inflamed (infl.) to total parenchyma areas were calculated using the ZEN software. ** and *** represent P values of <0.01 and <0.001, respectively.
