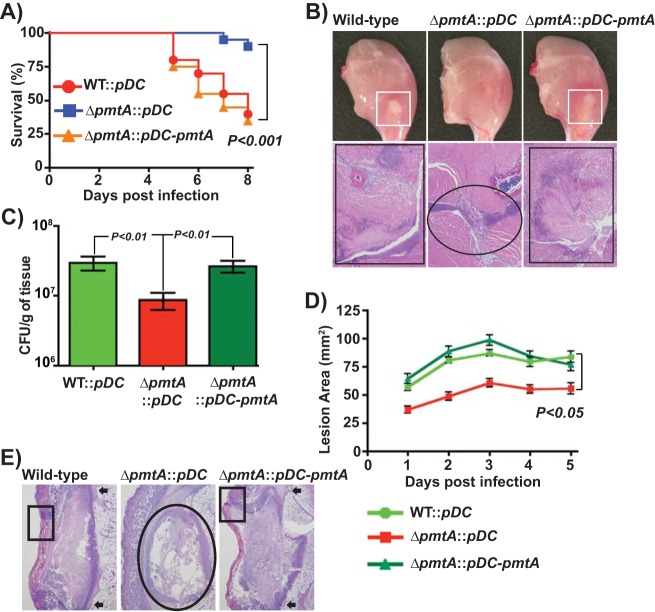
FIG 5.
PmtA is critical for survival during infection and GAS virulence. (A) Twenty outbred CD-1 mice per strain were injected intramuscularly with 1 × 107 CFU of each strain. Shown is a Kaplan-Meier survival curve with P values derived by a log rank test. (B) Macroscopic (top) and histopathological (bottom) analyses of hind-limb lesions from mice infected with the indicated strains at 48 h postinfection. Areas of host tissue damage are boxed (white boxes). Areas of disseminated lesions in the WT and trans-complemented strains are boxed (black box), whereas confined, less destructive lesions are circled. (C) Twenty mice were infected intramuscularly, and mean CFU recovered from infected muscle tissue at 96 h postinfection are shown, with P values as determined by a t test. (D) Twenty immunocompetent hairless mice were infected with the indicated strains, and the lesion area produced by each strain was determined. The lesion area was measured daily and graphed (means ± standard error of the means). The P value was derived by a log rank test. (E) Histopathological analysis of subcutaneous lesions of mice infected with the indicated strains at 48 h postinfection. Areas of disseminated lesions and ulcerations on the skin surfaces of mice infected with the WT and trans-complemented strains are boxed, whereas confined, less destructive lesions in tissues infected with the ΔpmtA mutant are circled.