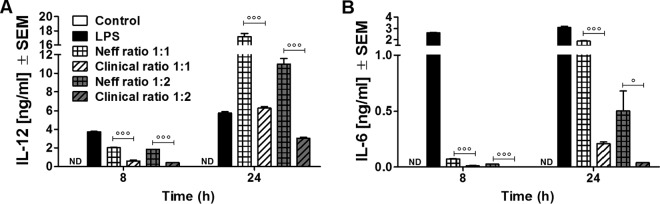
FIG 2.
Release of IL-12 (A) and IL-6 (B) at 8 and 24 h after coincubation with A. castellanii trophozoites. Murine macrophages (1 × 106) obtained from BALB/c mice were challenged with 1 × 106 or 5 × 105 trophozoites of either the Neff strain (Neff ratio 1:1 and Neff ratio 1:2, respectively) or the clinical isolate (Clinical ratio 1:1 and Clinical ratio 1:2, respectively). LPS at a concentration of 200 ng/ml was used as a positive control, whereas uninfected macrophages (Control) were considered the negative control. The experiment was repeated twice. Results represent the mean ± standard error (n = 3). One-way ANOVA was applied for each time point, and Tukey's multiple-comparison test was performed to evaluate differences within the condition means at each time point. In the graphs, significant differences between Neff and clinical strains are indicated as follows: °, P < 0.05; °°°, P < 0.0005. Values below the detectable levels are indicated in the graphs as ND (not detected). Note that the Acanthamoeba Neff strain induces higher levels of macrophage proinflammatory cytokines than the Acanthamoeba clinical isolate. This event was observed at both the early time points (8 h after coincubation) and the later time points (24 h after coincubation).