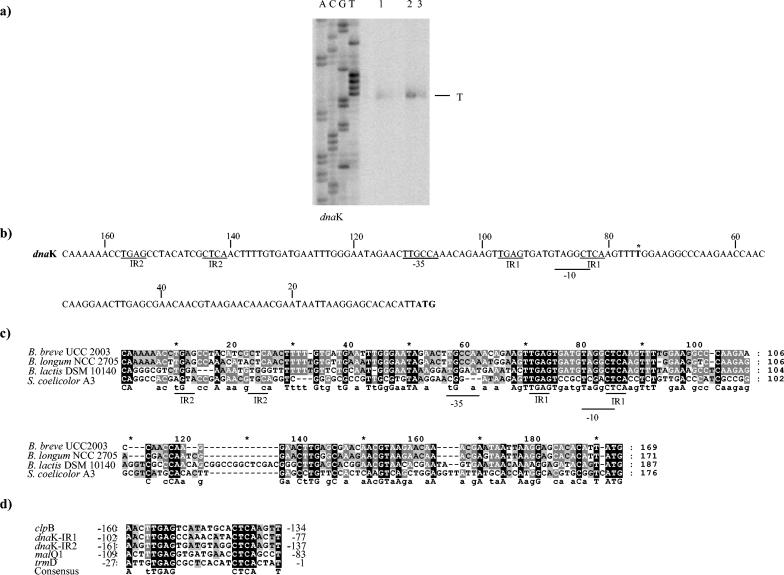
FIG. 4.
Determination of the dnaK transcription initiation site of B. breve UCC 2003 by primer extension analysis. (a) Primer extension results obtained by using an oligonucleotide targeting the 5′ end of dnaK. Lane 1, primer extension product obtained by using mRNA extracted from cells grown at 37°C; lane 2, primer extension product obtained by using mRNA extracted from cells grown with 0.7 M NaCl; lane 3, primer extension product obtained by using mRNA extracted from cells grown at 43°C. (b) Putative promoter sequences for the dnaK gene. The −10 and −35 putative hexamers are underlined; boldface type with an asterisk indicates the transcription start point; and boldface type without an asterisk indicates the start codon. IR1 and IR2 are putative regulator sequences. (c) Comparison of the promoter regions of four dnaK genes from different members of the Actinobacteridae. Shaded residues indicate that the level of identity for the sequences is 50% or higher. (d) Alignment of consensus IR sequences from B. longum NCC 2705. Identical nucleotides are shaded. The numbers indicate positions relative to the translational start site.