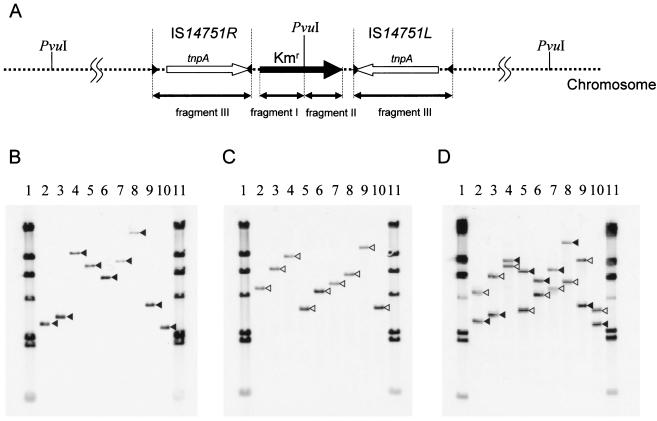
FIG. 8.
Transposition of minicomposite Tn14751 into C. glutamicum. (A) Schematic physical map of the minicomposite Tn14751 transposon in the chromosome of C. glutamicum mutants. The positions of Southern hybridization probes (fragments I, II, and III) are indicated by bidirectional arrows below the map. PvuI sites are indicated above the map. The tnpA genes and inverted repeat sequences of IS14751L and IS14751R are indicated by open arrows and solid arrowheads, respectively. The kanamycin resistance gene is represented by a solid arrow. (B to D) Southern hybridization of PvuI-digested chromosomal DNA from nine minicomposite Tn14751 integrated C. glutamicum mutants with fragment I (B), fragment II (C), and fragment III (D) as the probes. Lanes 1 and 11, λ HindIII molecular weight marker; lanes 2 to 10, nine minicomposite Tn14751 integrated C. glutamicum mutants (CGR732-1 to CGR732-9). (B) The solid arrowheads indicate the migration positions of hybridization signals when fragment I was the probe. (C) The open arrowheads indicate the migration positions of hybridization signals when fragment II was the probe. (D) Southern hybridization with fragment III as the probe resulted in two bands in each lane (lanes 2 to 10). The migration positions of signals corresponding to signals shown in panel B are indicated by solid arrowheads, and the migration positions of signals corresponding to signals shown in panel C are indicated by open arrowheads.