Figure 3.
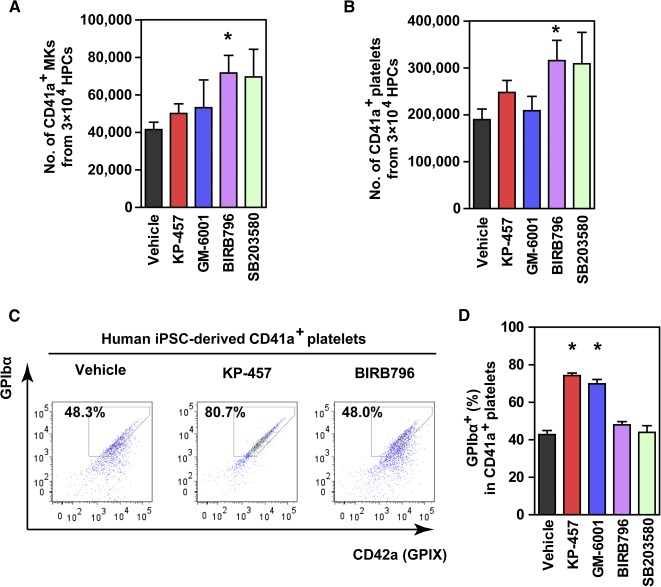
GPIbα shedding from platelets generated in vitro from iPSC‐MKs was effectively suppressed by KP‐457 but not by p38 MAPK inhibitors. (A) Numbers of CD41a+ iPSC‐derived MKs. Human HPCs were incubated for 8–10 days in differentiation medium supplemented with stem cell factor, thrombopoietin, heparin, and/or inhibitors at 37°C, followed by flow cytometric analysis. p38 MAPK inhibitors increased MK yields, whereas KP‐457 and GM‐6001 had only minor effects. (B) Numbers of CD41a+ iPSC platelets. (C) Representative FACS dot plots of platelets generated from iPSC‐derived HPCs in the presence of KP‐457 or BIRB796. (D) Percentages of the GPIbα+ population in CD41a+ platelets. Metalloproteinase inhibitors, including KP‐457, but not p38 MAPK inhibitors, enabled GPIbα retention by iPSC‐derived platelets. ∗, p < .05 vs. vehicle group by Dunnett’s test, n ≥ 4. Abbreviations: FACS, fluorescence‐activated cell sorting; GP, glycoprotein; HPC, hematopoietic progenitor cell; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell; MAPK, mitogen‐activated protein kinase; MK, megakaryocyte.
