Figure 4.
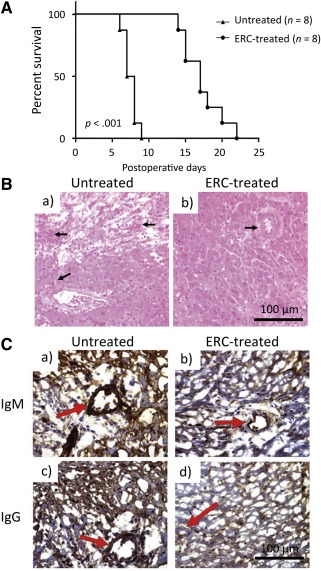
ERCs attenuate murine cardiac allograft rejection. (A): Prolonged murine cardiac allograft survival of ERC‐treated recipients. C57BL/6 (H‐2b) hearts were heterotopically transplanted to BALB/c (H‐2d) mice. In treated groups, recipients were injected i.v. with ERCs (1 × 106 cells per mouse) 24 hours after cardiac transplantation. Beating of the grafted heart was monitored daily by direct abdominal palpation. End‐point for each animal represents cessation of cardiac impulses (n = 8). p value was determined by log‐rank survival test (∗, p < .001, survival proportions of recipients treated with ERCs vs. survival proportions of recipients without treatment). (B): Histology of cardiac allografts recipients. On postoperative day 8, the rejection time‐point for the untreated group, grafts were harvested and evaluated by H&E staining of paraffin sections (n = 8). (Ba): Cardiac grafts from untreated transplant recipients. (Bb): Grafts from ERC‐treated recipients. Arrows indicate intravascular and/or interstitial changes in heart grafts. (C): Intragraft IgM and IgG deposition in cardiac transplant recipients. Antibody deposition in grafted hearts at the time of sacrifice was observed by immunohistochemistry specific for either IgM or IgG (n = 8). (Ca): Cardiac grafts from untreated transplant recipients. (Cb): Grafts from ERC‐treated recipients. Arrows indicate IgM deposition around vessels. (Cc): Grafts from untreated transplant recipients. (Cd): Grafts from ERC‐treated recipients. Arrows indicate IgG deposition around vessels. Scale bars = 100 μm. Abbreviation: ERC, endometrial regenerative cell.
