Figure 7.
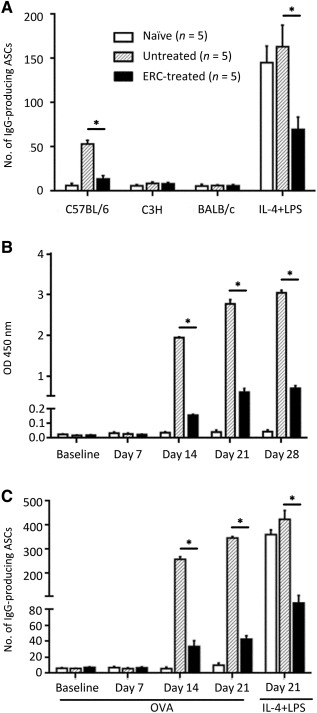
ERCs inhibit donor‐specific and total IgG ASCs in cardiac allograft recipients, as well as the levels of anti‐OVA antibody and the frequency of anti‐OVA antibody‐secreting B cells of OVA‐vaccinated mice. (A) To identify anti‐donor‐specific ASCs, splenic CD19+ B cells of allograft recipients (postoperative day 8) or naïve BALB/c mice were exposed to various cell lysates (donor C57BL/6, third‐party C3H, or syngeneic BALB/c) coated on ELISpot plates (n = 5). Uncoated wells supplemented with IL‐4 (100 U/ml) and LPS (2 μg/ml) served as positive controls to indicate the total IgG‐secreting cells within the splenic CD19+ B‐cell pool. (B): Anti‐OVA antibody within the circulation of OVA‐vaccinated mice. IgG anti‐OVA antibody titers within the various serum samples collected from mice immunized with ovalbumin‐aluminum hydroxide and naïve mice (days –1, 7, 14, 21, 28; n = 5) were determined by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay. (C): To identify anti‐OVA‐specific ASCs, splenic CD19+ B cells of OVA‐vaccinated, or naïve BALB/c, mice were harvested at days 0, 7, 14, and 21 and exposed to OVA‐coated ELISpot plates (n = 5). Uncoated wells supplemented with IL‐4 (100 U/ml) and LPS (2 μg/ml) served as positive controls to indicate the total IgG‐secreting cells within the splenic CD19+ B‐cell pool at day 21 postpriming with OVA. (A–C): Graphs represent mean ± SE of three separate experiments.∗, p < .001 determined by one‐way analysis of variance. Abbreviations: ASCs, antibody‐secreting cells; ERC, endometrial regenerative cell; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; OD, optical density; OVA, ovalbumin.
